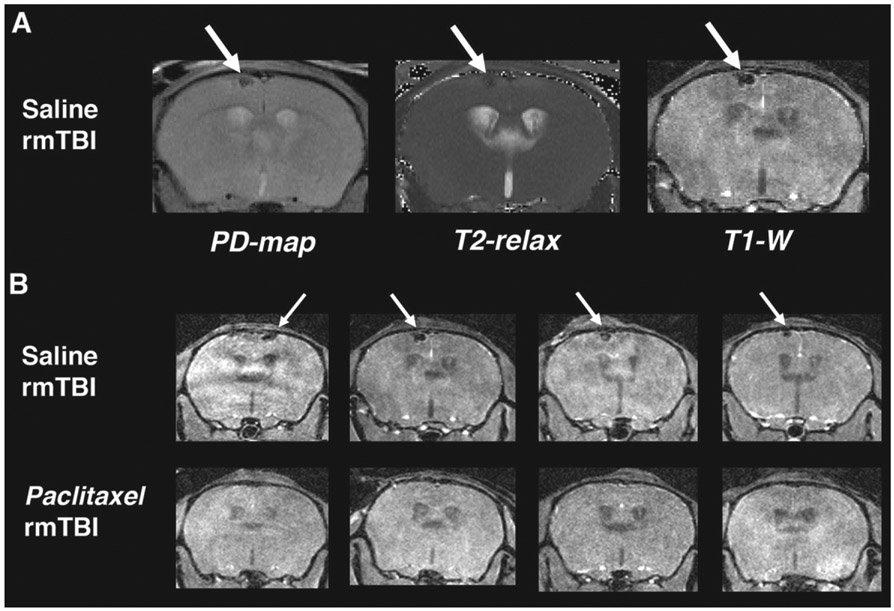
Fig. 3.
Paclitaxel prevents brain lesions associated with rmTBI. MR imaging was acquired at 4 days post-rmTBI to assess injury and response to paclitaxel treatment in vivo. A) Left to right: Proton Density mapping (PD-map), T2-relaxation quantitative image (T2-relax) and T1-weighted image (T1-W) from the same saline-treated mouse (coronal view). Green arrows indicate a dark spot in the cortex just below the impacted region. Spot is dark in all 3 images indicating a likely tissue strain microbleed. B) T1-W imaging of saline- (top row) and paclitaxel-treated (bottom row) from 4 subjects of each group. 100% (8/8) saline-treated subjects had microbleed lesion at 4 days post injury and 0% (0/6) of the paclitaxel-treated showed evidence of the lesion.