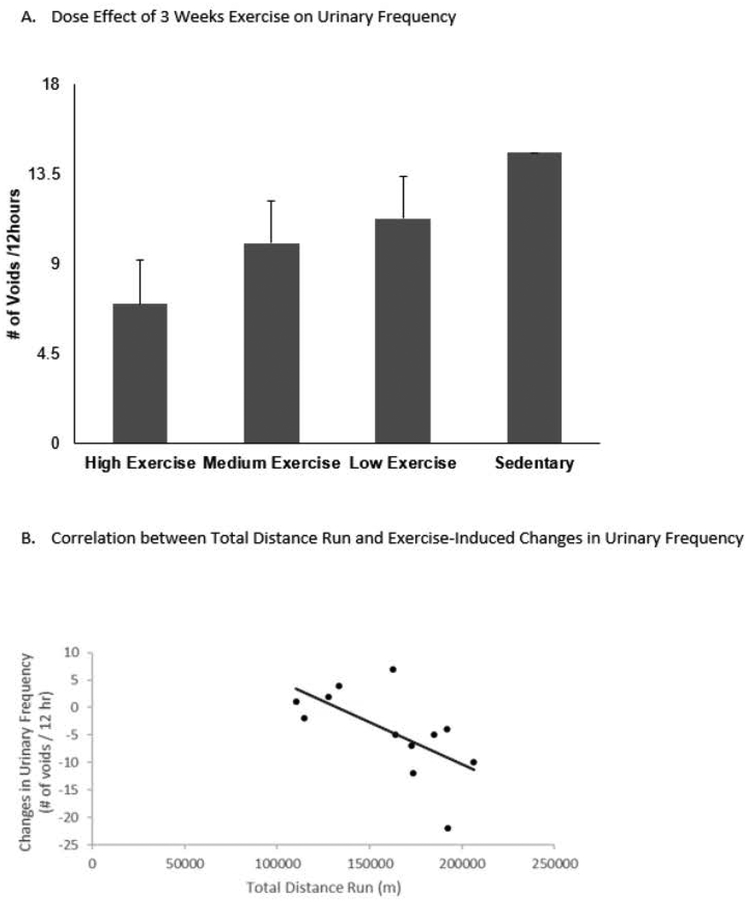
Figure 2:
A. Dose effect of 3 weeks exercise on urinary frequency by comparing to sedentary group. After 3 weeks exercise, both the medium exercise and high exercise groups had significant decreases in urinary frequency related to the amount of exercise they performed in a multivariable linear regression model controlling for water consumption (p=0.003 high exercise, p=0.05 medium exercise). B. Correlation between total distance run and exercise-induced changes in urinary frequency. Exercise-induced changes in urinary frequency showed statistically significant, negative correlation with total distance run over 3 weeks (Pearson’s r=−0.62, p=0.03).