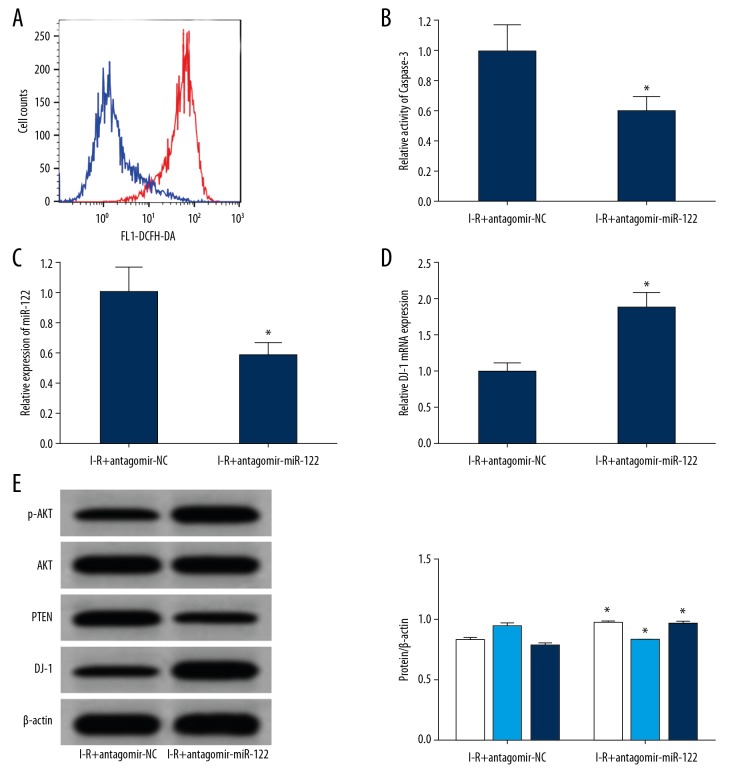
Figure 5.
MiR-122 significantly reduced DJ-1 expression and alleviates ischemia-reperfusion induced brain injury. (A) Flow cytometry detection of ROS content in 2 groups of rats (the bnlue line is I-R+antagomir NC and the red line is I-R+antagomir miR-122) (B) Spectrophotometry detection the caspase-3 enzyme activity in the 2 groups of brain tissues. (C) qRT-PCR detected the expression of miR-122 in rat brains. (D) qRT-PCR detected the expression of DJ-1 mRNA in rat brains. (E) Western blot detected protein expression in brain tissues (the white represents p-Akt/Akt, the light blue line represents PTEN, and the dark blue line represents DJ-1). * P<0.05 compared with the agomir control group. Each experiment was repeated 3 times. Flow testing showed that compared with the antagomir-NC group, the content of ROS in the brain tissues of the antagomir miR-122 group was significantly decreased (A), and the activity of caspase-3 in the brain tissues of the rats decreased significantly (B). The results of qRT-PCR showed that the expression of miR-122 in the brain tissues of the antagomir miR-122 group was significantly lower than the antagomir-NC group (C), while the expression of DJ-1 mRNA increased significantly (D). The results of western blot analysis showed that the expression of DJ-1 and p-AKT in the brain tissues of the antagomir miR-122 group was significantly higher than the antagomir-NC group, while the expression of PTEN protein decreased significantly (E). I-R group – ischemia-reperfusion damage model; ROS – reactive oxygen species; qRT-PCR – quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction.