Figure 2.
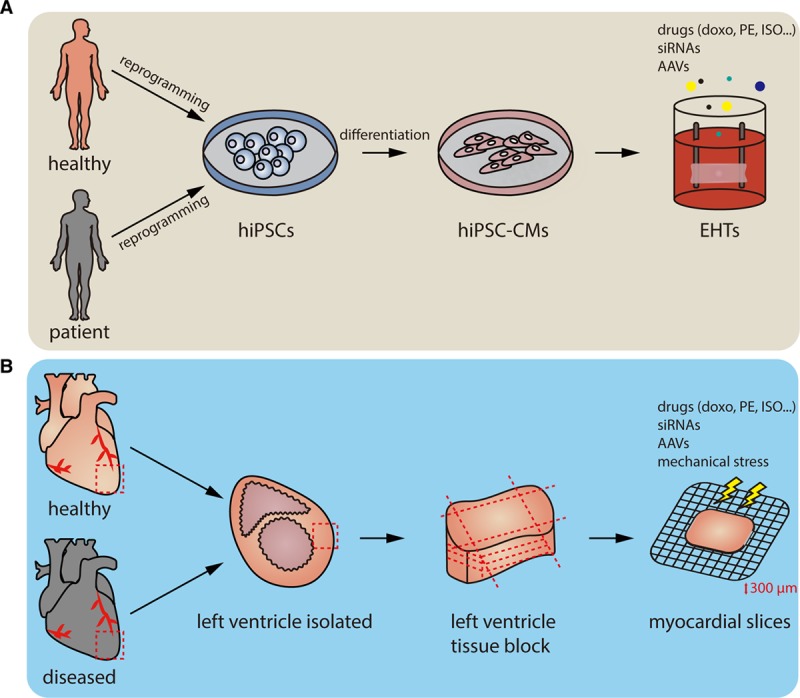
Workflow of 2 3-dimensional ex vivo models, engineered heart tissues (EHTs), and living myocardial slices. A, Somatic cells are isolated from human blood cells or skin cells, reprogrammed into human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs), and differentiated into hiPSC-derived cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-CMs). The hiPSC-CMs are seeded onto the scaffolds to generate beating EHTs. Compared with a 2-dimensional cell culture system, EHTs exhibit a better structure and matured phenotypes that are similar to adult CMs. Through modifying the stiffness of the scaffold, different disease models, such as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, can be established. EHTs can further be tested for drugs or as gene modulation tools. Not only stemming from healthy humans, EHTs can also be made from patients suffering from heart disease for disease modeling. B, To prepare living myocardial slices, small or large mammalian hearts, including human hearts, are explanted. The left ventricles or other parts of the heart are then isolated and dissected into small tissue blocks. Hundred to four hundred micrometers myocardial slices are sliced and used for further functional studies, for example, by treating with different drugs or adjusting the voltage that stimulates the contraction of the myocardial slices. Similar to EHTs, the living myocardial slices could also be prepared from diseased animal models. Doxo indicates doxorubicin; ISO, isoproterenol; and PE, phenylephrine.
