Figure 6.
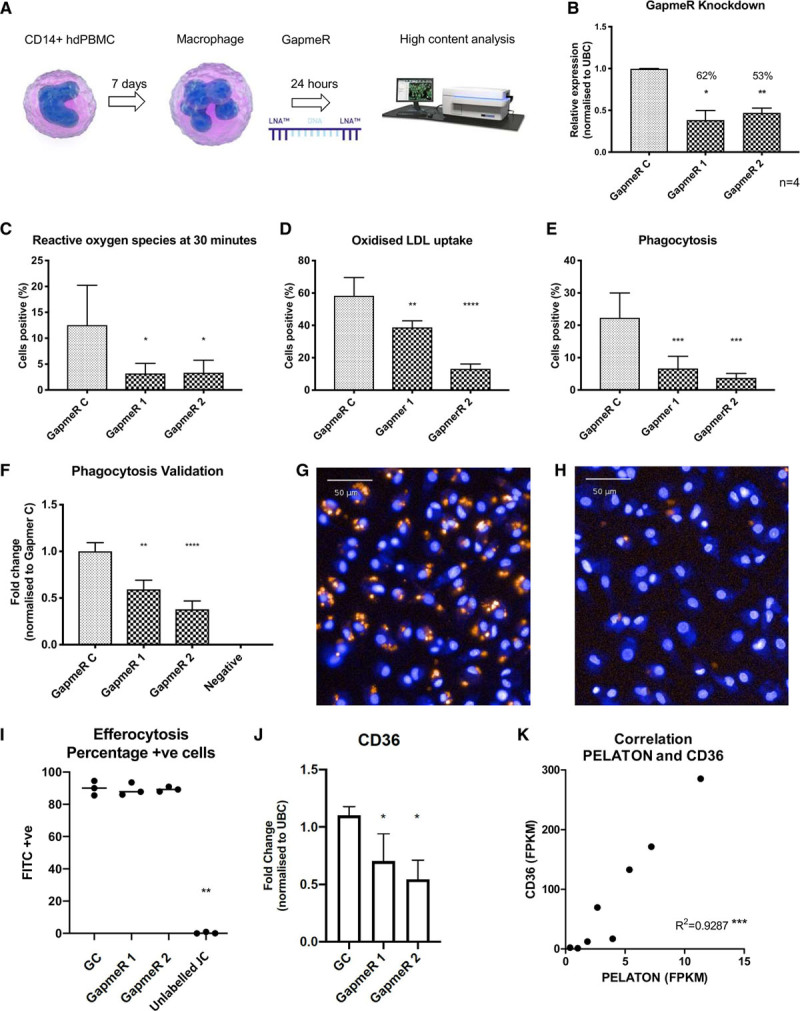
Effects of PELATON (plaque enriched lncRNA in atherosclerotic and inflammatory bowel macrophage regulation) knockdown on macrophage function. A, Schematic of high-content analysis workflow. B, GapmeR knockdown of PELATON in monocyte-derived macrophages. In high-content analysis, PELATON knockdown has a significant effect on (C) reactive oxygen species production after menadione induction, (D) oxidized LDL (low-density lipoprotein) uptake, and (E) phagocytosis. All HCA assays (C–K) performed in 5 wells per condition, 9 images per well, and n=2, pooled biological replicates. F, Validation of phagocytosis data assessed via pHrodo Zymosan particle uptake (orange beads), (3 biological replicates on different days, 11 to 14 wells per condition, 9 to 21 images per well assessed). Hoechst nuclear stain allows for cell detection. Representative images of (G) GapmeR control and (H) PELATON knockdown wells. I, Efferocytosis quantification following PELATON knockdown, calculated by the percentage of cells that have taken up Calcein labeled jurkat cells that had undergone apoptosis. J, Effect of PELATON knockdown on expression levels of CD36. K, Correlation of PELATON with CD36 expression in plaque based on fragments per kilobase million (FPKM) value from RNA sequencing data. Statistical analysis by 1-way ANOVA and multiple comparisons. FITC+ indicates fluorescein isothiocyanate positive cells; GC, gapmer control; HCA, high content analysis; hdPBMC, human-derived peripheral blood mononuclear cells; JC, Jurkat cells; and UBC, ubiquitin C.
