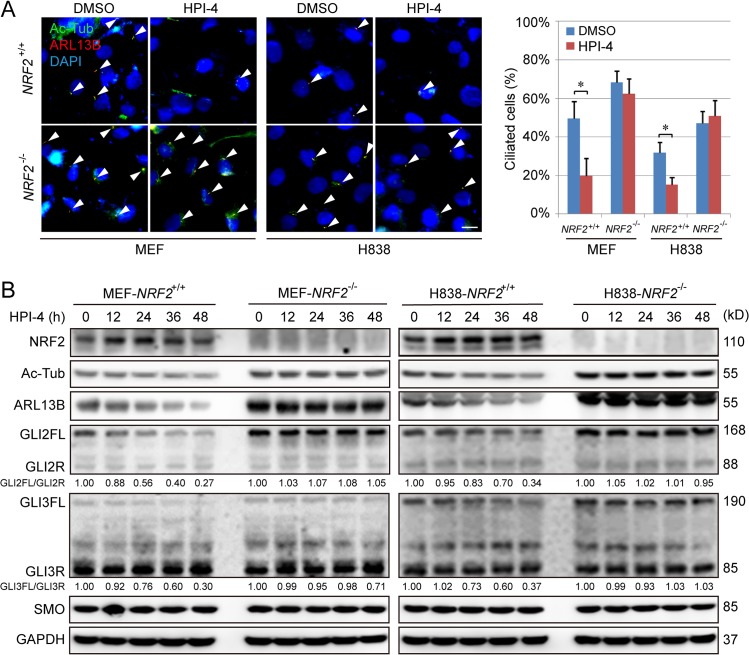
Fig 7. HPI-4 inhibits the formation of primary cilia in an NRF2-dependent manner.
(A) IF for Ac-Tub (green) and ARL13B (red) in MEF and H838 cell lines treated with HPI-4 (20 μM) for 48 h. Both NRF2+/+ and NRF2−/− cell lines were analyzed, the percentage of Ac-Tub/ARL13B-positive cells in 6 random fields was summarized, and total cell number was determined by DAPI stain. (Scale bar = 10 μm.) (B) Immunoblot analysis of NRF2, Ac-Tub, ARL13B, and Hh signaling pathway expression in different NRF2+/+ and NRF2−/− cell lines treated with HPI-4. Similar results were obtained in at least 3 independent experiments. Results are expressed as mean ± SD. A t test was used to compare the various groups, and p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. *p < 0.05 compared between the two groups. Ac-Tub, acetylated tubulin; ARL13B, ADP-ribosylation factor-like protein 13B; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; Hh, hedgehog; HPI-4, hedgehog pathway inhibitor-4; IF, immunofluorescence; MEF, mouse embryonic fibroblast; NRF2, nuclear factor-erythroid 2-like 2; SMO, smoothened.