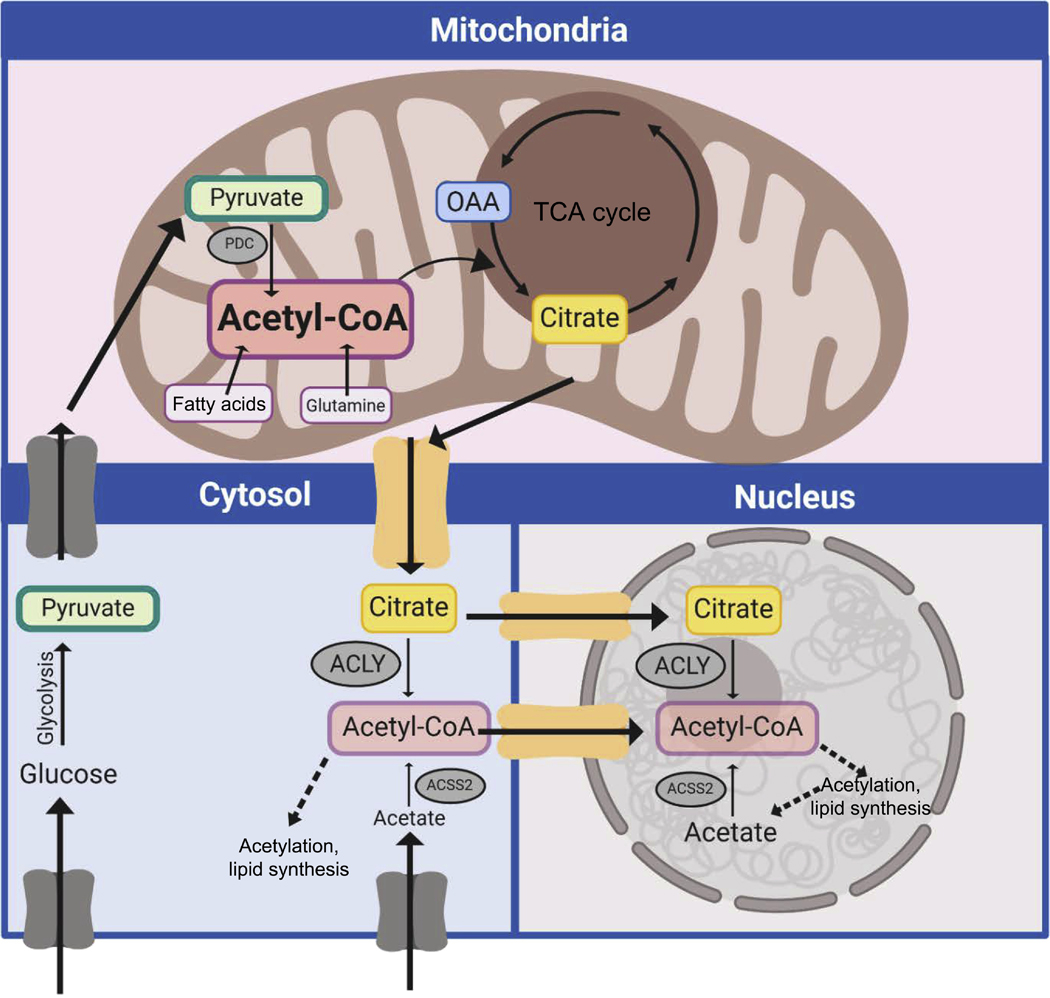
Figure 3:
The compartmentation of acetyl-CoA. Acetyl-CoA can be generated in different compartments of the cell including the mitochondria, cytosol and nucleus. The pool of mitochondrial acetyl-CoA is higher and not in equilibrium with the cytosolic-nuclear pool. Citrate export from the mitochondria can be re-converted to acetyl-CoA by the action of the enzyme ACLY. Moreover, acetate, taken up from the extracellular milieu or produced intracellularly, can also generate acetyl-CoA by the action of the enzyme ACSS2. ACLY and ACSS2 are found in the cytosol and nucleus. In the nucleus, these enzymes are believed to generate locally high concentrations of acetyl-CoA, presumably near sites of active chromatin acetylation.