Fig. 2. Detection of cutaneous IgG binding to mycolactone by quantitative ELISA.
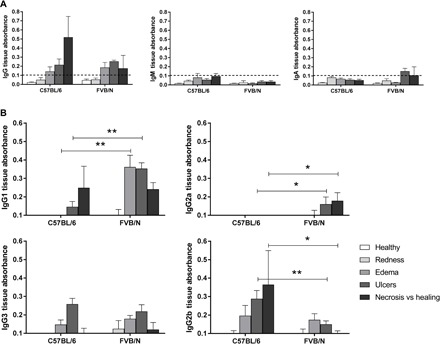
Each well of an ELISA MaxiSorp plate was coated with 3 ng of mycolactone, and the Ig concentrations of cutaneous tissue samples were normalized before their addition to the plate. Antibodies binding to mycolactone on the plate were recognized by horseradish peroxidase (HRP)–conjugated secondary antibodies. (A) Detection of IgG, IgM, and IgA and (B) IgG1, IgG2a, IgG3, and IgG2b recognizing the mycolactone in cutaneous tissue from FVB/N and C57BL/6 mice at various stages of infection (healthy, redness, ulcer, necrosis, or healing) (n = 3 to 5 mice per mouse strain). The detection limit was an absorbance of 0.1. The histograms show the means ± SD. *P < 0.5, **P < 0.01 (Mann-Whitney U test).
