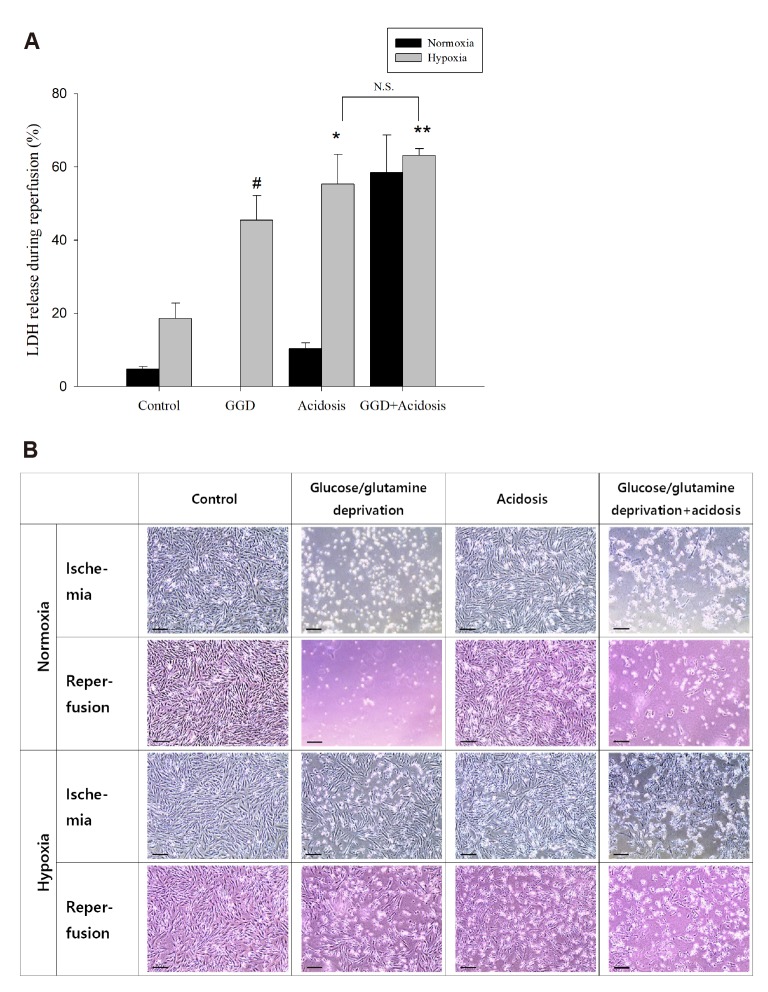
Fig. 5. Acidosis during hypoxia significantly induced reperfusion damage.
To produce media with pH 6.4 under 5% CO2, 2.4 mM NaHCO3, obtained from the Henderson-Hasselbach equation, was added to DMEM (D5030). In the control group, 24 mM NaHCO3 was added to achieve pH 7.4. Therefore, we added 21.6 mM Na-lactate to match the osmolality of the media used to induce acidosis in the control group. As a result, we used the media, which is made for simulating lactic acidosis. Media pH was measured 7.4–7.5 in the control group and 6.4–6.5 in the acidosis group. Cell passage used in these experiments was below 20. Data are expressed as means ± S.D. (n = 3) (*p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01vs. control under hypoxia, #p < 0.05 vs. glucose/glutamine deprivation + acidosis under hypoxia). GGD, glucose/glutamine deprivation; N.S., not significant. Scale bar: 200 µm.