Fig. 2. Proposed Cytc binding sites of cardiolipin, ATP, bc1 complex, COX, and Apaf-1.
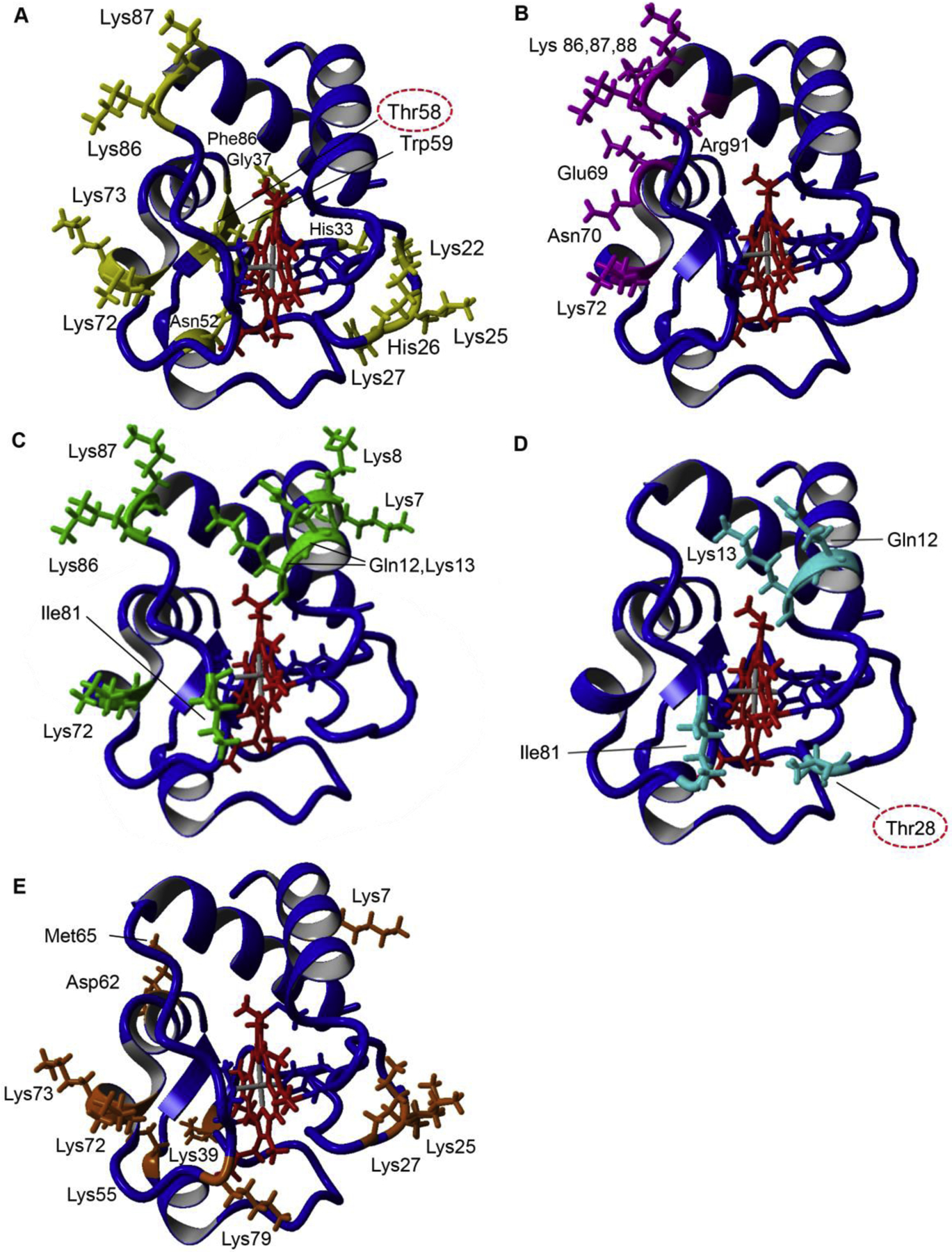
A: Cardiolipin binding sites of Cytc (yellow). Lys72, Lys73, Lys86, Lys87 (A-site) (Kagan et al., 2009), Lys22, Lys25, His26, Lys27, His33 (L-site) (Kagan et al., 2009), Asn52 (C-site) (Rytomaa and Kinnunen, 1994), Phe36, Gly37, Thr58, Trp59, and Lys60 (N-site) (O’Brien et al., 2015). B: ATP binding pocket of Cytc (magenta). Arg91 (Craig and Wallace, 1993; Tuominen et al., 2001), Glu69, Asn70, Lys72, Lys86, Lys87, Lys88, (McIntosh et al., 1996). C: COX binding sites of Cytc (green) were selected if defined as binding residues in at least two out of four publications, two docking simulations and two kinetic studies. Lys7, Lys8, Gln12, Lys13, Lys72, Ile81, Lys86, Lys87 (Roberts and Pique, 1999; Ferguson-Miller et al., 1978; Sato et al., 2016; Scharlau et al., 2019). D: bc1 complex core binding sites of Cytc (cyan) based on the yeast bc1-Cytc crystal structures and converted to mammalian Cytc residues. Gln12, Lys13, Thr28, Ile81(Lange and Hunte, 2002; Solmaz and Hunte, 2008). E: Apaf-1 binding sites of Cytc (orange), Lys7, Lys25, Lys39, Asp62, Met65 (Yu et al., 2001), Lys72 (Kluck et al., 2000), Lys27, Lys55, Lys73, Lys79 (Cheng et al., 2016). Amino acids that have been identified to be phosphorylated and are part of a binding site are circled.
