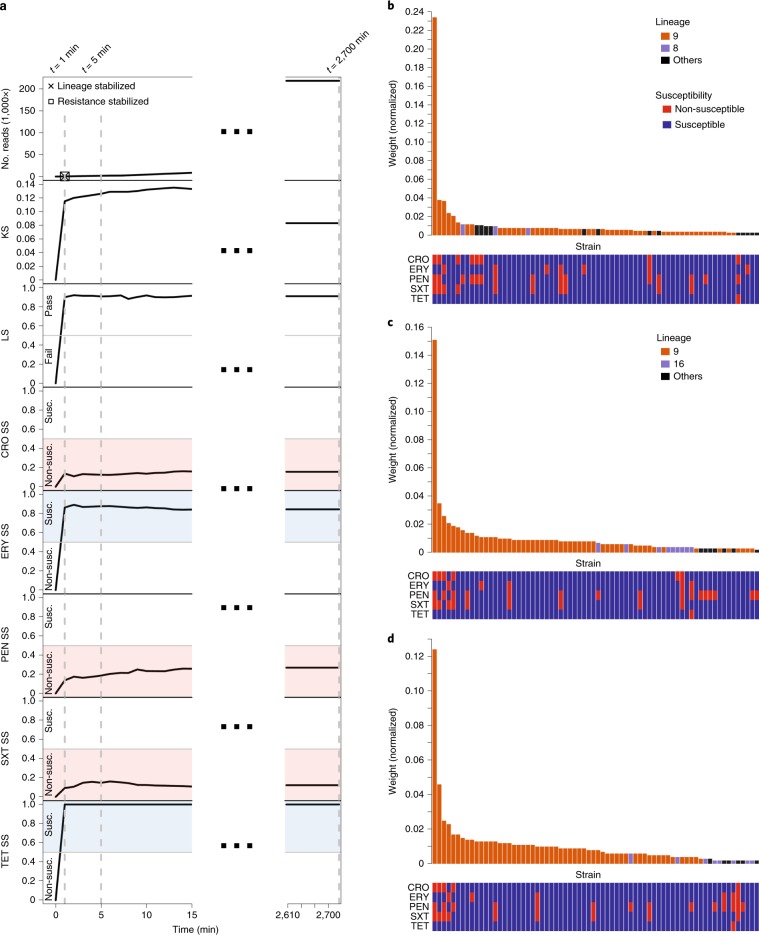
Fig. 2. RASE obtains stable predictions of antibiotic resistance or susceptibility and lineage within minutes for an isolate of a pneumococcal 23F clone (SP06).
a, The number of reads, LS, KS and SS for individual antibiotics as a function of time from the start of sequencing. In the top left plot, the times of stabilization are shown for the predicted lineage and susceptibility or resistance to all antibiotics (ceftriaxone (CRO), erythromycin (ERY), benzylpenicillin (PEN), trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole (SXT) and tetracycline (TET)). Blue and red colours correspond to susceptibility (Susc.) and non-susceptibility (Non-susc.) calls, respectively. The dashed lines mark selected time points (1 min, 5 min and the end of sequencing (2,700 min)). b–d, Similarity rank plots for selected time points: 1 min (b), 5 min (c) and the end of sequencing (2,700 min; d). The bars correspond to the 70 best-matching strains in the database and display the normalized weights, which serve as a proxy to the inverted genetic distance. They are arranged by rank and coloured according to the presence in the predicted, alternative or another lineage. The panels underneath each chart display the resistance profiles of the strains.