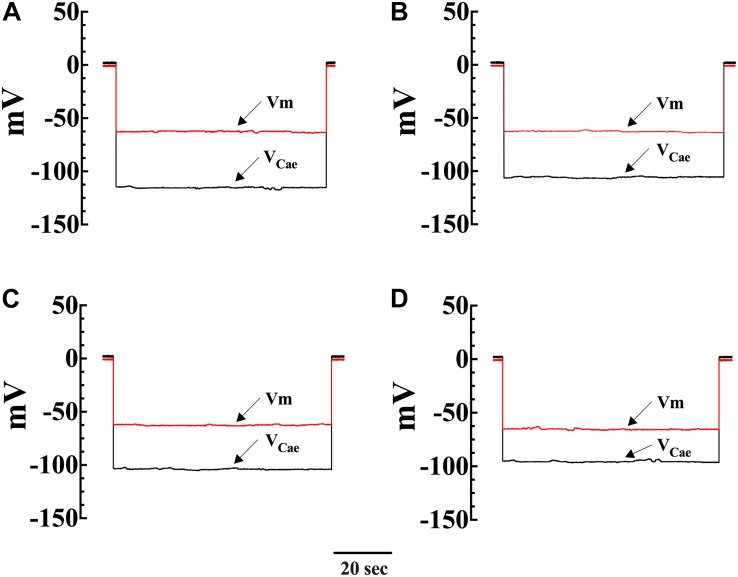
FIGURE 2.
Simultaneous measurements of Vm and [Ca2+]i in single smooth muscle cells from control Wt and mdx mice. Effects of OAG. Vm is the membrane potential recorded with a conventional microelectrode filled with 3 M KCI, and VCae is the potential recorded with the calcium-selective electrode after the subtraction of Vm. VCae potential represents cell intracellular [Ca2+]. In Wt, [Ca2+]i was 124 nM, and the Vm was –62 mV before OAG treatment and represents the cell intracellular [Ca2 + ] (A). After incubation in OAG 100 μM [Ca2+]i increased to 187 nM with no effect on Vm (–63 mV) (B). The measurements of Vm and [Ca2+]i before and after OAG treatment were carried in the same muscle cell. In the mdx muscle cell Vm: was –62 mV and [Ca2+]i was 258 nM before OAG (C) and after OAG incubation, [Ca2+]i rose to 492 nM after OAG, with no change in Vm (–65 mV) (D). The determinations of Vm and [Ca2+]i before and after OAG treatment were carried in two distinct muscle cells.