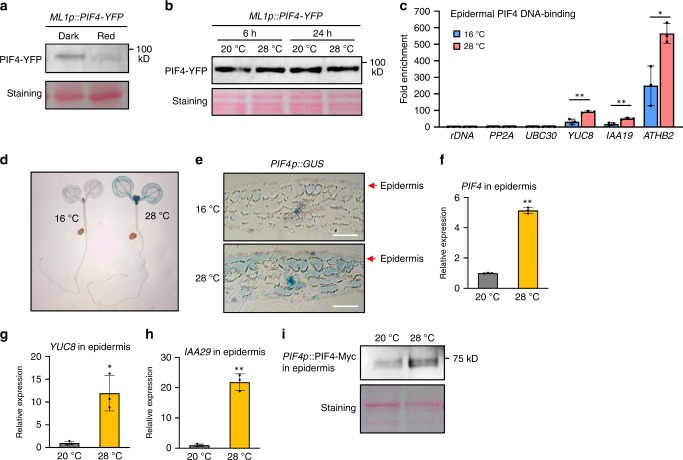
Fig. 6. Both epidermal PIF4 DNA-binding and epidermal PIF4 mRNA expression is increased at high temperatures.
a Red light induces the degradation of epidermal PIF4 protein. ML1p::PIF4-YFP;pifq seedlings were grown in the dark and transferred under red light for 2 h before harvesting. Immunoblotting was probed using an anti-GFP antibody. Ponceau S staining is shown for equal loading. b High temperature effects on the stability of epidermal PIF4 protein. ML1p::PIF4-YFP;pifq seedlings were grown under white light constitutively at 20 °C or grown at 20 °C and shifted to 28 °C for 6 or 24 h. Immunoblotting was probed using an anti-GFP antibody. Ponceau S staining is shown for equal loading. c ChIP assays showing epidermal PIF4 DNA-binding is increased by high temperatures. WT and ML1p::PIF4;pifq seedlings kept at 16 °C or shifted to 28 °C for 24 h were used for ChIP assays. Enrichment of DNA was calculated as the ratio between ML1p::PIF4;pifq and WT control, normalized to that of the rDNA gene as an internal reference. Error bars indicate s.d. (n = 3). ** P < 0.01 and * P < 0.05 (two-tailed Student’s t-test). d, e The effects of high temperatures on the expression of PIF4p::GUS. PIF4p::GUS seedlings were grown under white light constitutively at 16 °C or grown at 16 °C and shifted to 28 °C for 24 h. Cross-sections of cotyledons of seedlings are shown in e. Scale bars = 50 μm. f–h The expression of PIF4 and its target genes is increased by high temperatures in the epidermis. Wild-type seedlings were grown 20 °C or were shifted to 28 °C for 24 h. Total RNA was extracted from the isolated epidermal tissues. Gene expression levels were normalized to APX3 and presented as values relative to that of wild type at 20 °C. Error bars indicate s.d. (n = 3). *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 (two-tailed Student’s t-test). i The level of PIF4-Myc under the control of PIF4 promoter is increased by high temperatures in the epidermis. Epidermal tissues were isolated from PIF4p::PIF4-Myc;pifq seedlings grown at 20 °C or exposed to 28 °C for 24 h. PIF4-Myc protein in the isolated epidermis was determined by immunoblotting using an anti-Myc antibody. Ponceau S staining is shown for equal loading. The experiments (a, b, and i) were repeated at least two times with similar results. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.