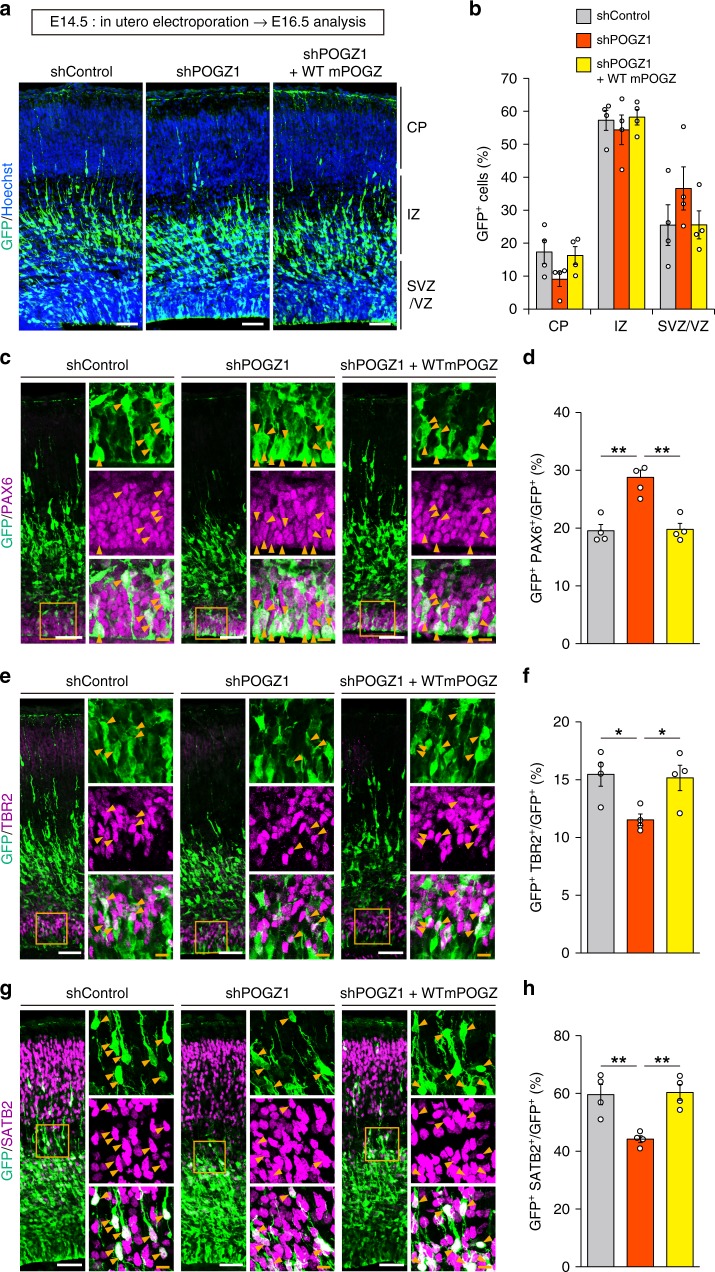
Fig. 3. POGZ regulates the neuronal differentiation of mouse cortical neural stem cells.
a Slight, non-significant migration defects caused by shRNA-mediated knockdown of Pogz in E16.5 mouse cortices electroporated at E14.5. CP cortical plate; IZ intermediate zone; SVZ subventricular zone; VZ ventricular zone; E embryonic day. Scale bars, 50 μm. b Quantification of GFP+ cells in each layer (each n = 4). CP cortical plate; IZ intermediate zone; SVZ subventricular zone; VZ ventricular zone. c Increased number of PAX6+ NSCs caused by Pogz knockdown in E16.5 mouse cortices electroporated at E14.5. d Quantification of PAX6+ cells (each n = 4). e Decreased number of TBR2+ differentiated IPs caused by Pogz knockdown in E16.5 mouse cortices electroporated at E14.5. f Quantification of TBR2+ cells (each n = 4). g Decreased number of SATB2+ differentiated neurons caused by Pogz knockdown in E16.5 mouse cortices electroporated at E14.5. h Quantification of SATB2+ cells (each n = 4). c, e, g Right panels, magnifications of the areas outlined with orange boxes. Arrowheads indicate co-labeled cells. White scale bars, 50 μm; orange scale bars, 10 μm. b Two-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Bonferroni–Dunn post hoc tests, F4, 27 = 1.861. d, f, h One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni–Dunn post hoc tests; d F2, 9 = 18.37; f F2, 9 = 5.710; h F2, 9 = 11.91. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. Data are presented as the mean ± s.e.m.