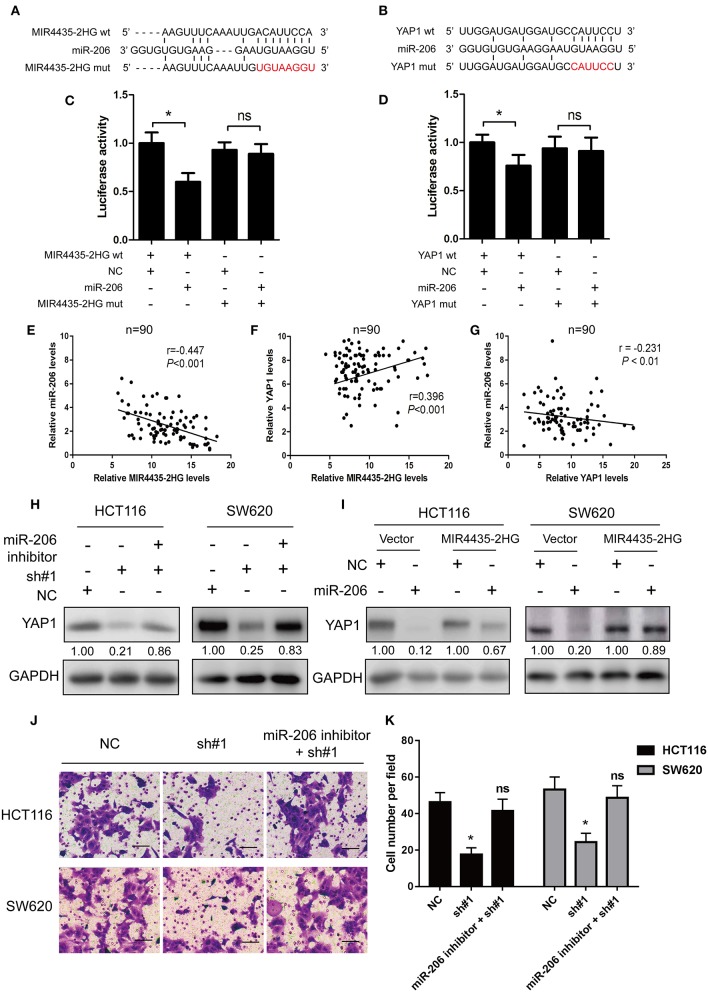
Figure 6.
MIR4435-2HG was a molecular sponge for miR-206 and controlled the miR-206 target YAP1. (A) Predicted sequences of miR-206-binding sites within MIR4435-2HG. MIR4435-2HG wt, miR-206, and MIR4435-2HG mutants (mut) sequences were used in Luciferase reporter gene assays. (B) Estimated sequences of miR-206-binding sites within the 3′-UTRs of YAP1 and sequences of YAP1 and YAP1 3′-UTR mutants (mut) were adopted here. (C) Luciferase reporter gene assays were adopted for assessing the interaction between miR-206 and MIR4435-2HG in SW620 cells. (D) Luciferase activity in SW620 cells underwent co-transfection with miR-206 mimics and luciferase reporters containing wild-type YAP1 or mutated 3′-UTR-driven reporter constructs. (E–G) Correlation between MIR4435-2HG, miR-206, and YAP1 expression in CRC and normal colon specimens as detecting by real-time PCR (n = 90). (H) Western blotting assay of YAP1 protein expression in YAP1 knockdown in HCT116 and SW620 cells with and without miR-206 inhibitor. (I) Western blot analysis of YAP1 protein expression following expression of empty vector (NC) or MIR4435-2HG and treating process with miRNA negative control or miR-206 mimics. (J,K) The migration ability after MIR4435-2HG knockdown with and without miR-206 inhibitor in HCT116 and SW620 cells. *P < 0.05.