Fig. 3.
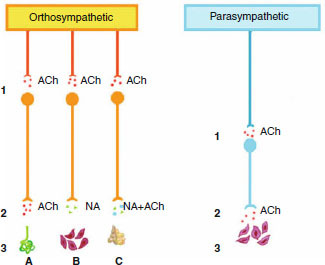
The autonomic nervous system is divided into orthosympathetic (sympathetic) and parasympathetic arms. Anatomical distinction between the two arms is related to the different lengths of the post-ganglionic neurons, which are longer in the orthosympathetic than in the parasympathetic arm. In the parasympathetic arm, the ganglion is closer to the target organ (3). For both systems, acetylcholine (ACh) is the neurotransmitter at the pre-ganglionic synapses (1). ACh is the neurotransmitter at the post-ganglionic synapses in the parasympathetic arm and for orthosympathetic fibres to the eccrine sweat glands (2, A). All other post-ganglionic synapses (B) of the orthosympathetic arm are noradrenergic (NA). Both NA and ACh (NA + ACh) pathways are involved in post-ganglionic transmission at the suprarenal level (C).
