Fig. 1.
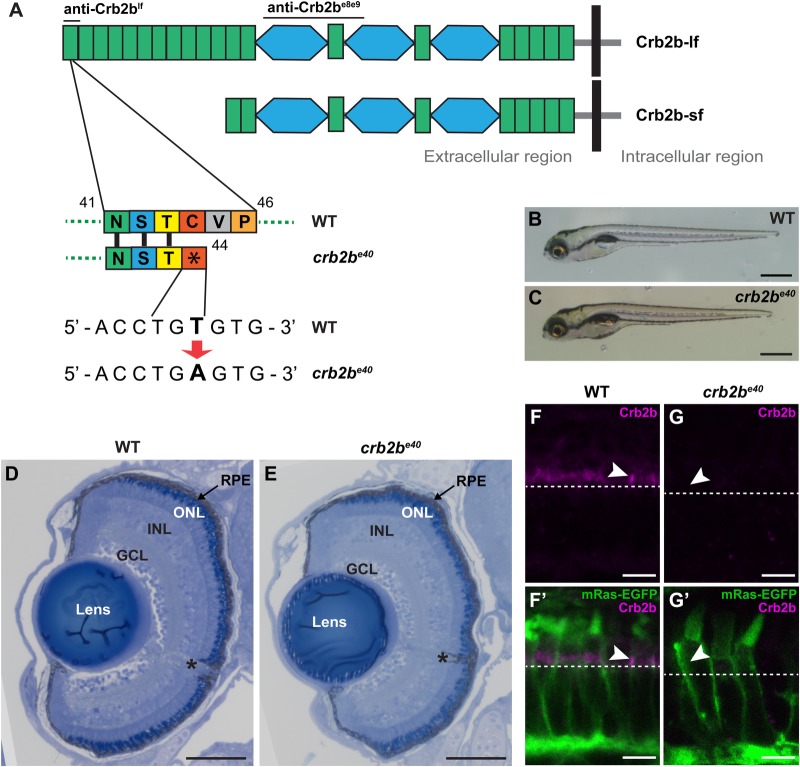
crb2be40 mutants are homozygous viable and develop normal eyes. (A) Schematic illustration of the long and short isoforms of Crb2b, Crb2b-lf and Crb2b-sf. Green rectangles, EGF-like domains; light blue hexagons, domains with similarity to the globular domain of laminin A (LamG domain). Bars above the protein indicate the regions used as antigens for anti-Crb antibodies. In the crb2be40 allele, a T to A transversion translates to an early stop codon at amino acid position 44 of the protein, resulting in truncated Crb2b-lf. (B,C) Brightfield images of WT (B) and crb2be40 (C) zebrafish larvae at 5 dpf. Mutant larvae have overall normal appearance. (D,E) Transverse retinal sections stained with Toluidine Blue show normal lamination of the retina of crb2be40 (E) larvae in comparison to WT (D) at 5 dpf. Asterisk denotes the optic nerve. GCL, ganglion cell layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium. (F–G′) Confocal images of transverse retinal sections of larvae at 3 dpf stained with rabbit anti-Crb2be8e9 in the Tg(bactin:mRas-EGFP) background. Crb2b is detected in the IS of WT PRCs (F,F′, white arrowheads), but not in crb2be40 mutant PRCs (G,G′). White dashed lines mark the position of the outer limiting membrane. Scale bars: (B,C) 1 mm; (D,E) 100 µm; (F–G′) 5 µm.