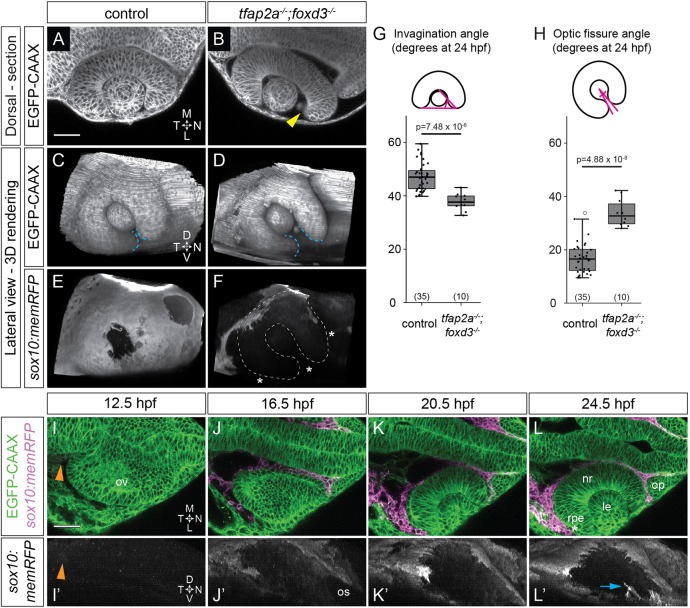
Fig. 1.
Optic cup morphogenesis requires neural crest. (A-F) Dorsal (A,B) and lateral (C-F) views of 24 hpf Tg(bactin2:EGFP-CAAX);Tg(sox10:memRFP) double-transgenic control and tfap2a;foxd3 mutant optic cups. A and B show single confocal sections at the dorsal-ventral midpoint of the lens. Arrowhead in B marks a gap where nasal retina fails to fully enwrap the lens. White dashed lines in F mark the optic cup boundaries. Blue dashed lines (C,D) mark the optic fissure margins. Asterisks in F indicate regions lacking neural crest. (G,H) Quantification of invagination angle (G) and optic fissure angle (H) measured as shown in inset diagrams. n (embryos) shown at base of graphs, from three experiments. P-values were calculated using one-way ANOVA with Tukey HSD post-hoc test. (I-L′) Time-lapse imaging (12.5-24.5 hpf) of a Tg(bactin2:EGFP-CAAX);Tg(sox10:memRFP) double-transgenic embryo. (I-L) Dorsal view, single confocal sections. (I′-L′) Lateral view, 3D rendering of magenta channel from same dataset. Arrowheads in I,I′ indicate RFP+ neural crest. Asterisk in L marks RPE between neural crest and neural retina. Arrow in L′ marks neural crest-derived cells entering the optic fissure. Scale bars: 50 μm. D, dorsal; L, lateral; le, lens; M, medial; N, nasal; nr, neural retina; op, olfactory placode; os, optic stalk; ov, optic vesicle; rpe, retinal pigment epithelium; T, temporal; V, ventral.