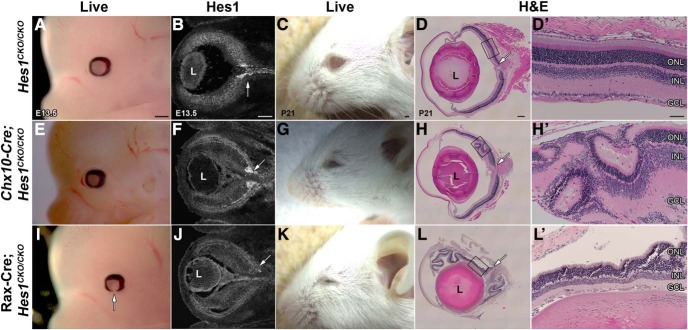
Figure 2.
Hes1 conditionally mutant ocular defects. A, E, I, Lateral views of E13.5 live embryos. Chx10-Cre;Hes1CKO/CKO eyes (E) are indistinguishable from control littermates (A). However Rax-Cre;Hes1CKO/CKO eyes have fully penetrant colobomas (arrow in I). B, F, J, Anti-Hes1 labeling of E13.5 cryosections indicates the identical loss of low, nonuniform expression from the retina of both Cre-mutants. However, Chx10-Cre;Hes1CKO/CKO eyes retain high, sustained Hes1 expression in the ONH (arrows in each panel). Rax-Cre;Hes1CKO/CKO uniquely exhibited an abnormal elongated shape to the retina (J). C, G, K, Gross examination of P21 eyes suggests microphthalmia in Chx10-Cre;Hes1CKO/CKO (G) and Rax-Cre;Hes1CKO/CKO (K) mutants. D, H, L, However, H&E-stained P21 sections at the level of the optic nerve support smaller eyes only for Rax-Cre;Hes1CKO/CKO. Both mutants have lamination defects and retinal rosettes (H), along with severe thinning of retinal layers (L). D′, H′, and L′ are higher magnifications of boxed areas in D, H, and L, respectively. L, lens; ONL, outer nuclear layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer. Scale bars: 50 μm in B, D, and D′ and 500 μm in A and C. n = 3 biologic replicates per age and genotype were evaluated.