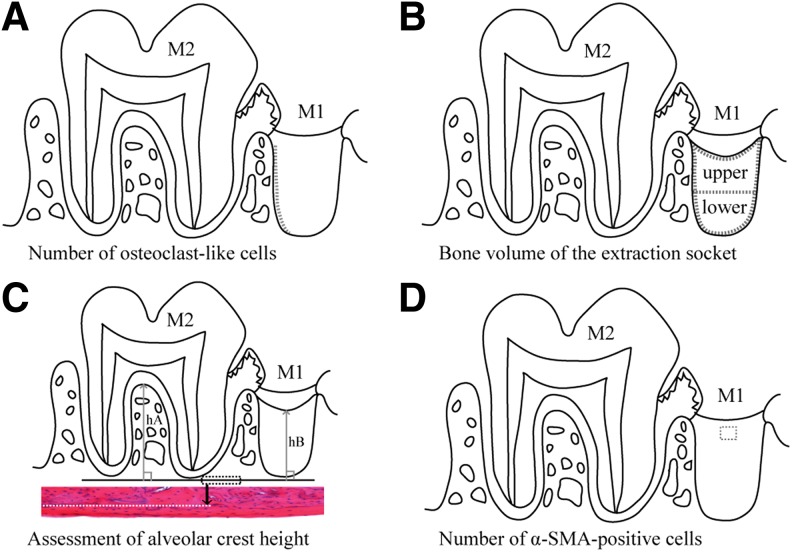
FIG. 2.
Morphological measurement methods. (A) Number of osteoclast-like cells. Length of the BS (dotted line) of the distal extraction socket wall was measured, and the number of the osteoclast-like cells on the surface was counted. The number of the cells per 1 mm on the surface of the extraction socket wall (N.Oc/BS) was then calculated on day 3 postextraction. (B) BV of the extraction socket. The extraction socket is divided into three parts (enclosed with dotted lines): the upper layer, the lower layer, and the whole (the upper+lower layers), and the ratio of the BV of new bone (cancellous bones) per TV in each area (BV/TV) was calculated on day 7 postextraction. (C) Assessment of alveolar crest height. Dotted rectangle shows the line of the inferior edge of the maxillary lamellar bone (reference line). H&E staining; original magnification × 100. The longest distance (hA) from the reference line perpendicular to the interradicular septum of the second molar (M2) and the shortest distance (hB) from the reference line to the surface layer of the new bone formed in the distal root socket of the extracted first molar (M1) were measured; hB/hA (mean ± standard deviation) was calculated as an index on day 21 postextraction. (D) Number of α-SMA-positive cells. α-SMA positive cells in a 150 × 150 μm square in the granulation tissue or the lamina propria in the surface layer of the socket (area within the dotted outline) of the first molar (M1) were counted on day 3 postextraction. BS, bone surface; BV, bone volume; H&E, hematoxylin–eosin; SMA, smooth muscle actin; TV, tissue volume.