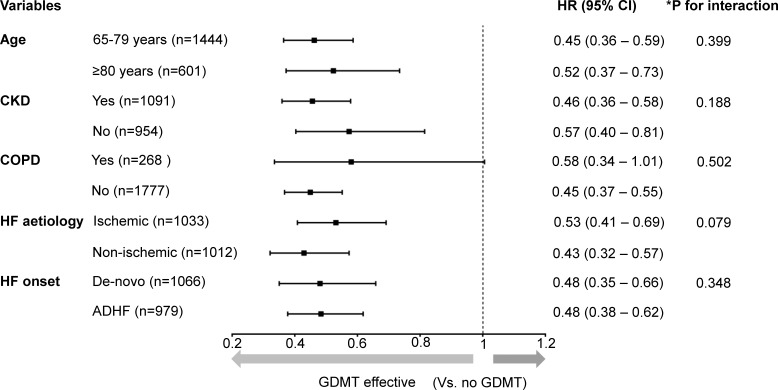
Figure 4.
Subgroup analysis. The HRs of medical therapy (ie, GDMT, beta-blockers only and RAS inhibitors only) compared with no GDMT for all-cause mortality in subgroups were calculated using multivariate Cox regression analysis. The forest plots demonstrate the HRs of GDMT versus no GDMT from the results. There was no significant interaction between the treatment strategy (no GDMT, beta-blockers only, RAS inhibitors only and GDMT) and diverse subgroups, and GDMT was associated with lower morality across subgroups. *The p for interaction indicates whether treatment strategy interacts with the subgrouping variable. It was calculated from multivariable Cox regression analysis that included the variables for treatment strategy, subgrouping variables, interaction term of the treatment strategy-by-subgrouping variable, sex, hypertension, diabetes, atrial fibrillation and prescription of mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists, digitalis and diuretics. CKD, chronic kidney disease; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; HF, heart failure; GDMT, guideline-directed medical therapy; RAS, renin–angiotensin system.