Figure 1.
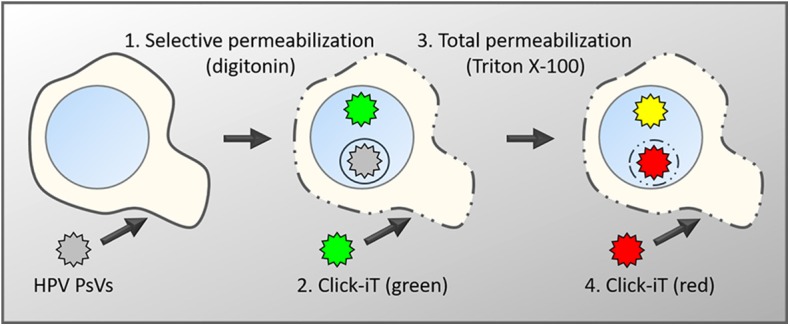
Schematic diagram of the differential staining technique. Keratinocytes are infected with PsVs, whose encapsidated DNA had been labeled with EdU during virus production (Ishii et al., 2010). After fixation, cells are differentially permeabilized with low concentrations of digitonin under conditions that will exclusively permeabilize membranes rich in cholesterol such as the plasma membrane and endocytic vesicles directly derived from the plasma membrane (1) (DiGiuseppe et al., 2016). Subsequently, accessible viral genome will be labeled with a green fluorescent dye using Click-iT chemistry (2). This is followed by a total permeabilization using high concentrations of Triton X-100 (3) and a second round of Click-iT reaction using a red fluorescent dye (4). Genomes accessible after the initial digitonin permeabilization will be labeled with both dyes and appear in yellow in fluorescent microscopy. Genomes residing in the lumen of intracellular membranes such as the TGN or transport vesicles will only be accessible to the red dye and therefore appear in red.
