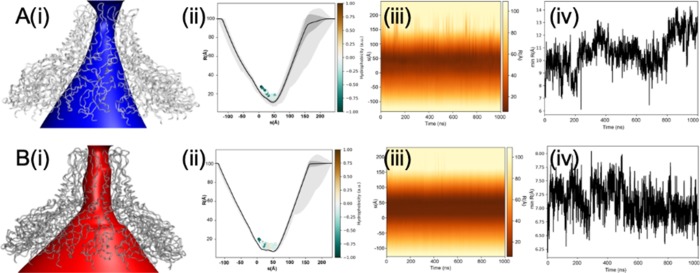
Figure 3.
Pore profiles of (A) wt-AtVirB10CTD and (B) mt-AtVirB10CTD from MD simulations. (i) Annotation of the solvent conduction pathway. (ii) Time-averaged radius profile calculated as a function of position, s, along the pore axis. Calculations were done over 2000 frames at an interval of 0.5 ns and drawn as a solid line (standard deviation as a gray band). Residues facing the pore for more than 50% of the simulation time are illustrated as dots and colored based on their hydrophobicity. (iii) Dynamic radius profile highlights the variation in pore dimensions over the course of the simulation. The pore is structured and displayed less variation in the mutant.(iv) Minimum pore radius over simulated time highlights stabilization of the pore in the mutant when compared with the wild type.