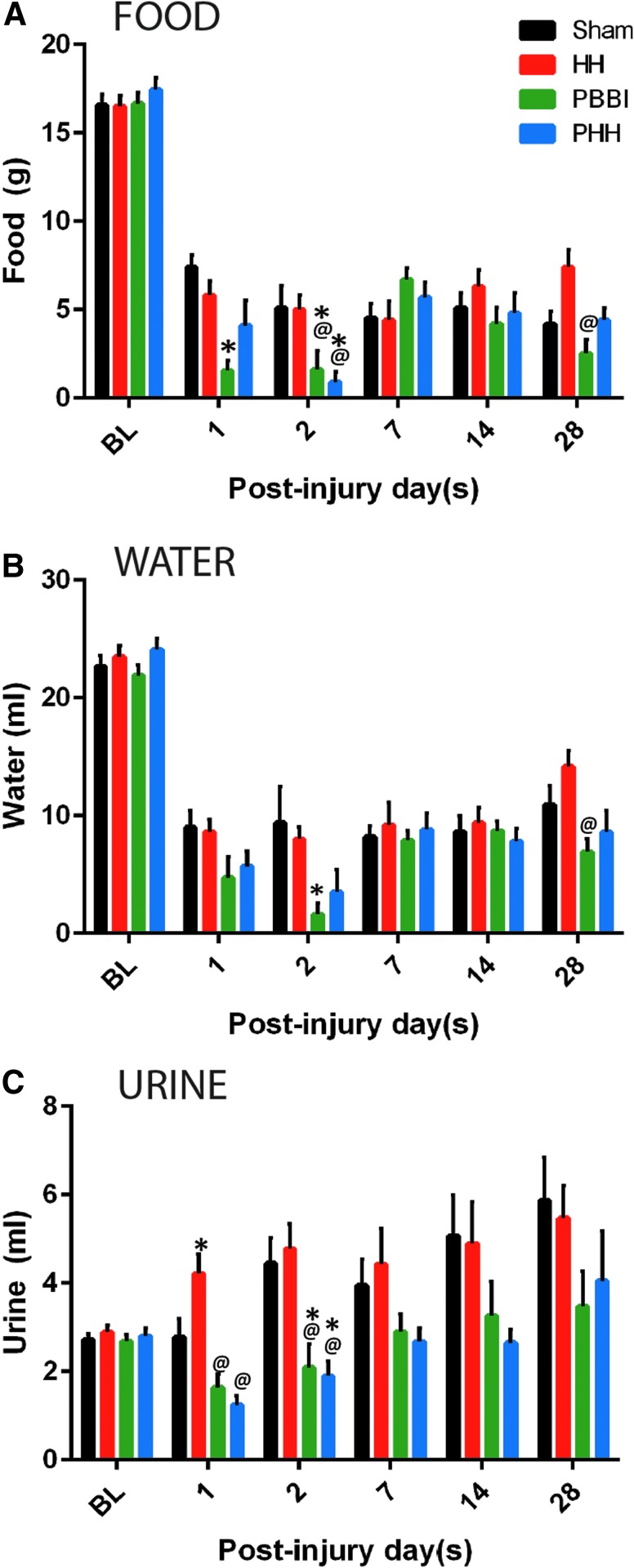
FIG. 1.
Food, water and urine levels following injury: Decreased food and water consumption were observed in rats following both polytrauma and penetrating ballistic-like brain injury (PBBI). Temporal changes in (A) food consumption, (B) water intake, and (C) urine output. Baseline (BL) data is from all 50 rats (10 rats from each time-point) per group and for the post-injury set it is n = 10 per group per time-point; p values for between-group analysis of variance was <0.008 for food, <0.019 for water and <0.001 for urine. *p < 0.05 vs. sham group; @p < 0.05 vs. hypoxemia and hemorrhagic shock (HH) group.