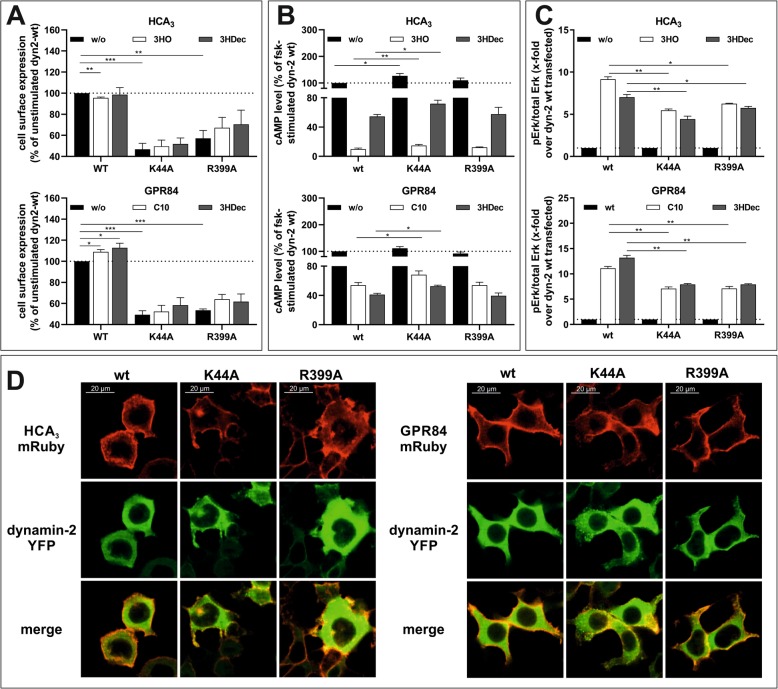
Fig. 3.
Effect of dyn-2 mutants on HCA3 and GPR84 cell surface expression, cAMP inhibitory signaling and ERK activation. a-c CHO-K1 cells were transiently co-transfected with HCA3 or GPR84 and dyn-2 wt, dyn-2 K44A or R399A mutants. a In comparison to dyn-2 wt co-transfected cells HCA3 and GPR84 cell surface expression was significantly reduced when K44A or R399A were co-transfected. b Basal activity of HCA3 but not GPR84 was diminished in presence of K44A. Agonist-induced (HCA3: 6.25 μM 3HO, 25 μM 3HDec; GPR84: 100 μM C10, 25 μM 3HDec) inhibition of forskolin-stimulated cAMP accumulation was reduced in presence of K44A compared to dyn-2 wt whereas R399A did not affect cAMP inhibitory signaling. c Agonist-induced increase of pERK/total ERK level of HCA3 (25 μM 3HO, 100 μM 3HDec) and GPR84 (25 μM C10, 25 μM 3HDec) was reduced in presence of K44A and R399A compared to dyn-2 wt. a-c Data is given as mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments each carried out in triplicates. * P ≤ 0.05; ** P ≤ 0.01, *** P ≤ 0.001 (d) Images of HEK293-T cells transiently co-expressing HCA3-mRuby (red) or GPR84-mRuby and dyn-2-YFP variants (green). In presence of dyn-2 wt, HCA3 was detected intracellularly and at the plasma membrane where it co-localized with dyn-2 wt. In case of co-expression of HCA3 with the dyn-2 mutants K44A and R399A, co-localization was detected in perinuclear vesicles as well as certain areas at the plasma membrane. GPR84 was in presence of all dyn-2 variants found mostly at the plasma membrane