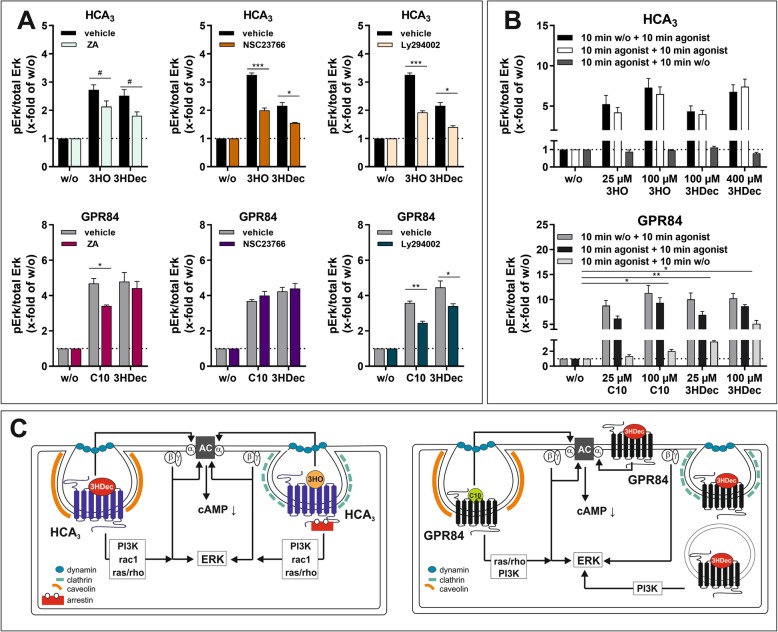
Fig. 6.
Components involved in HCA3 and GPR84 signal transduction. a, b Agonist-induced phosphorylation of endogenous ERK1/2 in cellular lysates of HCA3 or GPR84 transfected CHO-K1 cells in absence and presence of 25 μM ZA (zoledronic acid - inhibitor of ras/rho), 100 μM NSC23766 (inhibitor of rac1) and 25 μM Ly294002 (inhibitor of PI3K) was determined. a ZA, NSC23766 and Ly294002 partially inhibited the HCA3-induced ERK activation of both agonists. ZA and Ly 294,002 caused a significant reduction of the GPR84-mediated ERK activation by C10, whereas the ERK activation by 3HDec was only affected by presence of Ly294002. NSC23766 did not inhibit the GPR84-induced activation of ERK by either agonist. b Both, the 3HO- and 3HDec-induced ERK activation of HCA3 did not persist upon removal of agonist. The GPR84-mediated activation of ERK by 3HDec persisted, whereas the C10-induced activation was almost completely diminished 10 min past agonist removal. a, b pERK/total ERK of HCA3- or GPR84-transfected cells in absence of agonist is set 1, respectively. Data is given as mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments each carried out in triplicates. #P ≤ 0.1; * P ≤ 0.05; ** P ≤ 0.01; *** P ≤ 0.001. c 3HO- and 3HDec-induced cAMP inhibitory signaling of HCA3 was dependent on Gαi, Gβγ subunits and dyn (internalization). Signaling components involved in HCA3-mediated ERK activation by 3HO an 3HDec included Gβγ subunits, PI3K, rac1 and ras/rho. HCA3 activation by 3HO led to β-arrestin-2 recruitment, which was not the case for 3HDec. ERK signaling of HCA3 by 3HO involved clathrin and by 3HDec caveolin. GPR84 activation by C10 was dependent on Gαi, Gβγ subunits, dyn (internalization), caveolin, ras/rho and PI3K. In contrast, 3HDec-induced cAMP inhibitory signaling was not dependent on Gβγ subunits, dyn, caveolin or clathrin, thus internalization. ERK activation induced by GPR84 upon 3HDec stimulation persisted upon agonist removal and involved PI3K