Fig. 11:
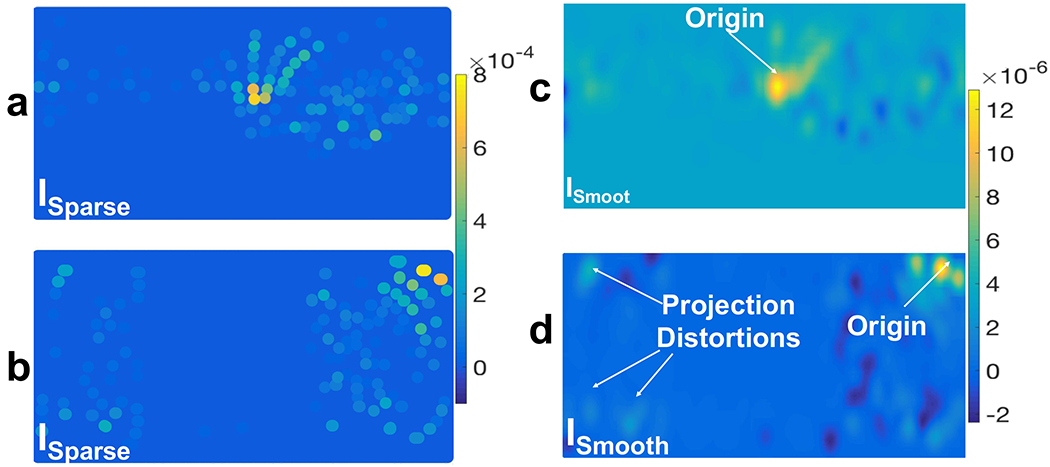
Cylindrical projection of preprocessed scalp EEG signals (SCorr) onto a 2D plane (ISparse in (a) and (b)) and their spatial interpolation (ISmooth in (c) and (d)) using a Gaussian spatial kernel with σ = 6.8 mm. In ISparse each dot indicates an EEG electrode location and its color indicates the corresponding amplitude of SXcorr (t = 10 min): a) a cylindrical projection which is oriented in a direction that captures the CSD wave in the middle of the plane and (c) is its spatially interpolated image; b) a cylindrical projection which is oriented normal to the previous one and, in this example, it captures the CSD wave near the boundary of the plane and causes distortion in the wavefronts and (d) is its corresponding interpolated ISmooth.
