Figure 2.
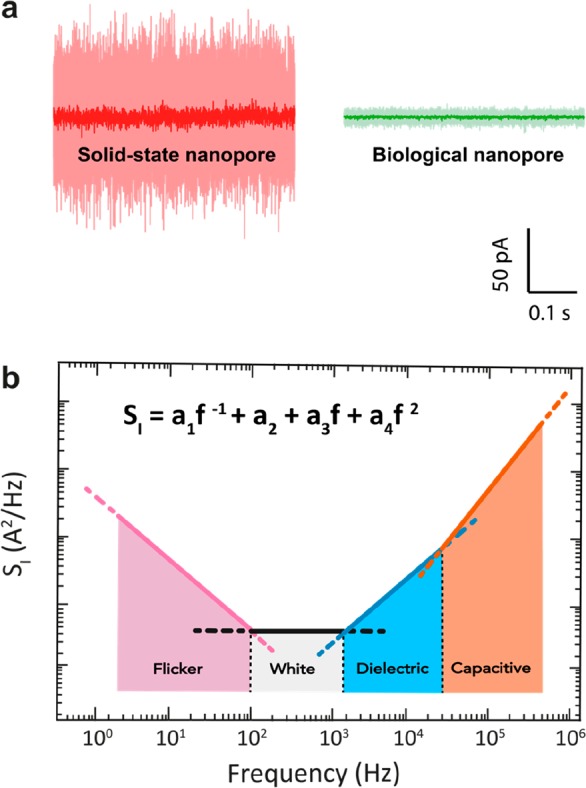
Ionic current noise in nanopores. (a) Example current traces for a 1.3 nm diameter solid-state SiNx nanopore (red) and a 1.4 nm diameter biological α-HL pore (green), performed at a constant applied bias of 100 mV in 1 M KCl buffer at pH 7 at a bandwidth of 10 kHz (light) and 1 kHz (dark). α-HL pore was measured using the typical Montal–Muller approach,47 with a bilayer diameter of ∼100 μm, as described by Maglia et al.3 The solid-state pore was fabricated on a Si-supported 20 nm-thick SiNx freestanding membrane using transmission electron microscopy. Currents through both pores were amplified with Axopatch 200B. (b) Schematic of the current PSD for a typical nanopore. Common types of noise are highlighted in the various frequency ranges.
