10.
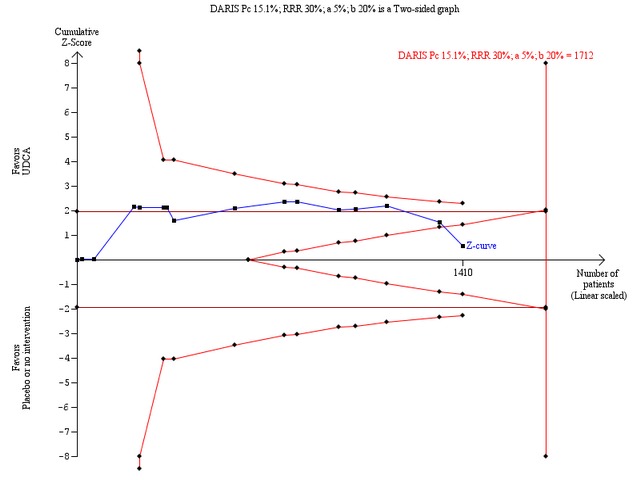
Trial sequential analysis of the random‐effects meta‐analysis of the effect of ursodeoxycholic acid versus placebo or no intervention on all‐cause mortality or liver transplantation. The trial sequential analysis is performed with an assumed control proportion of death of 15.1%, an anticipated relative risk reduction (RRR) of 30%, a type 1 error risk of 5% (two‐sided), and a power of 80% (a type 2 error risk of 20%) (b). The diversity‐adjusted required information size (DARIS) to detect or reject a RRR of 30% with a between trial heterogeneity of 37% is estimated to 1712 patients. The actually accrued number of patients is 1410, which is 82% of the required information size. The blue cumulative Z‐curve does not cross the red trial sequential alpha‐spending monitoring boundaries for benefit or harm. However, the boundaries for futility delineated by the trial sequential beta‐spending monitoring boundaries (the red inner wedge boundaries) are crossed. Accordingly, the red conventional boundaries (horizontal line at z =1.96 and z =‐1.96) for harm or benefit are not crossed. Therefore, there is no evidence to support that ursodeoxycholic acid influences mortality or transplantation. Moreover, a 30% RRR of mortality or transplantation can be rejected with the chosen error risks.
