Figure 1.
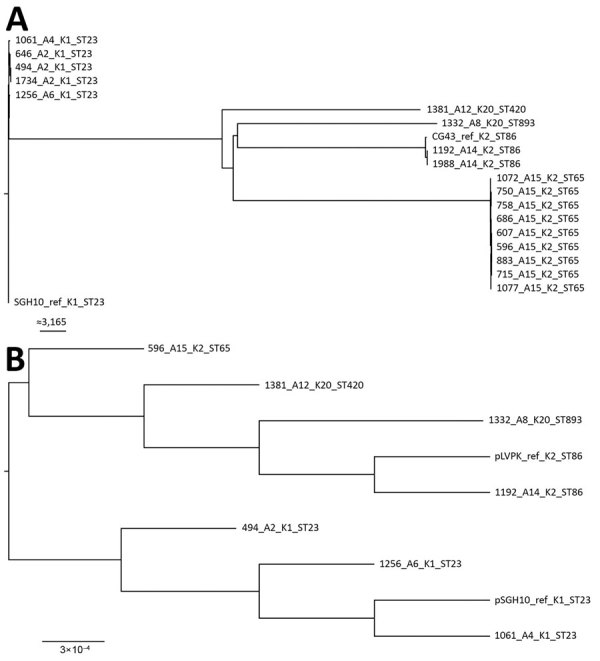
Maximum-likelihood trees of genes from carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates, Singapore, 2013–2015. A) Analysis generated using 63,297 single-nucleotide polymorphism sites in the core genome. The chromosomal sequence of SGH10 (GenBank accession no. CP025080) was used as reference. Isolates are closely related to hypervirulent strains SGH10 and CG43. Scale bar indicates number of single-nucleotide polymorphisms. B) Analysis generated from the alignment of K. pneumoniae virulence plasmids from the first isolates collected from different patients. The sequences of K. pneumoniae virulence plasmid pSGH10 (GenBank accession no. CP025081) was used as reference. Scale bar indicates nucleotide changes per base pair. Trees were drawn using FigTree version 1.4.4 (http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree) and rooted at the SGH10 branch. Labels indicate isolate no._patient no._K serotype_sequence type. Ref, reference; ST, sequence type.
