Figure 2.
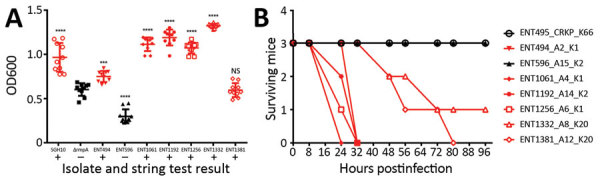
Hypervirulence assessment of first isolates from 7 patients with CRKP infections, Singapore, 2013–2015. A) Hypermucoviscosity of isolates as indicated by a low-speed centrifugation assay and the string test. For the centrifugation assay, Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates were grown in Luria broth overnight at 37°C and centrifuged (10 minutes at 2,000 × g), and OD600s of supernatants were measured. Each symbol represents the value for an individual clone (n = 10) from 3 independent experiments. Horizontal bars indicate means and error bars SDs. For the string test, K. pneumoniae were grown on sheep blood agar (2 days at 37°C). Red indicates a positive string test result. B) In vivo virulence in mice. Female C57BL/6J mice (7–8 weeks old, 3 mice/isolate) were injected with 1 × 105 CFU of bacteria by the intraperitoneal route. Every 8 or 16 hours, mice were checked and scored for death. If necessary, they were euthanized and counted as dead. The experiment was stopped at 96 hours postinfection. For each isolate, patient number and K serotype is indicated. CRKP, carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae; OD, optical density; NS, not significant. ***p = 0.0001; ****p<0.0001.
