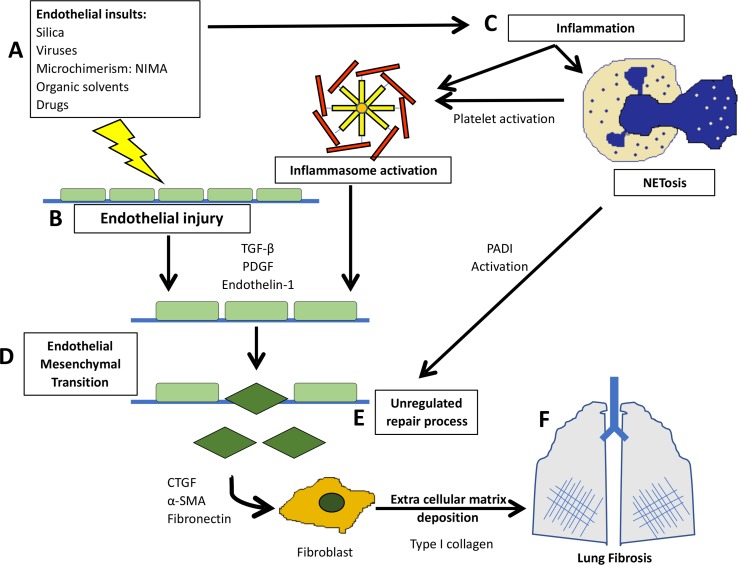
Figure 1.
In a background of genetic susceptibility, various environmental insults (A) lead to (B) endothelial injury and (C) Inflammation. (B) Endothelial activation leads to conversion of endothelial cells into mesenchymal progenitors (D). Also (C) inflammation causes NETosis and inflammasome activation that initiate a repair process that is imprinted on the fibroblasts (E). All these lead to conversion of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts and extracellular matrix deposition in the lung interstitium (F) and thus fibrotic lung disease.
(NIMA: Non-inherited maternal antigens; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-β; PDGF: Platelet derived growth factor; CTGF: Connective Tissue Growth Factor; α-SMA : α- Smooth muscle actin; PADI: Peptidyl arginine deiminase)