Figure 2:
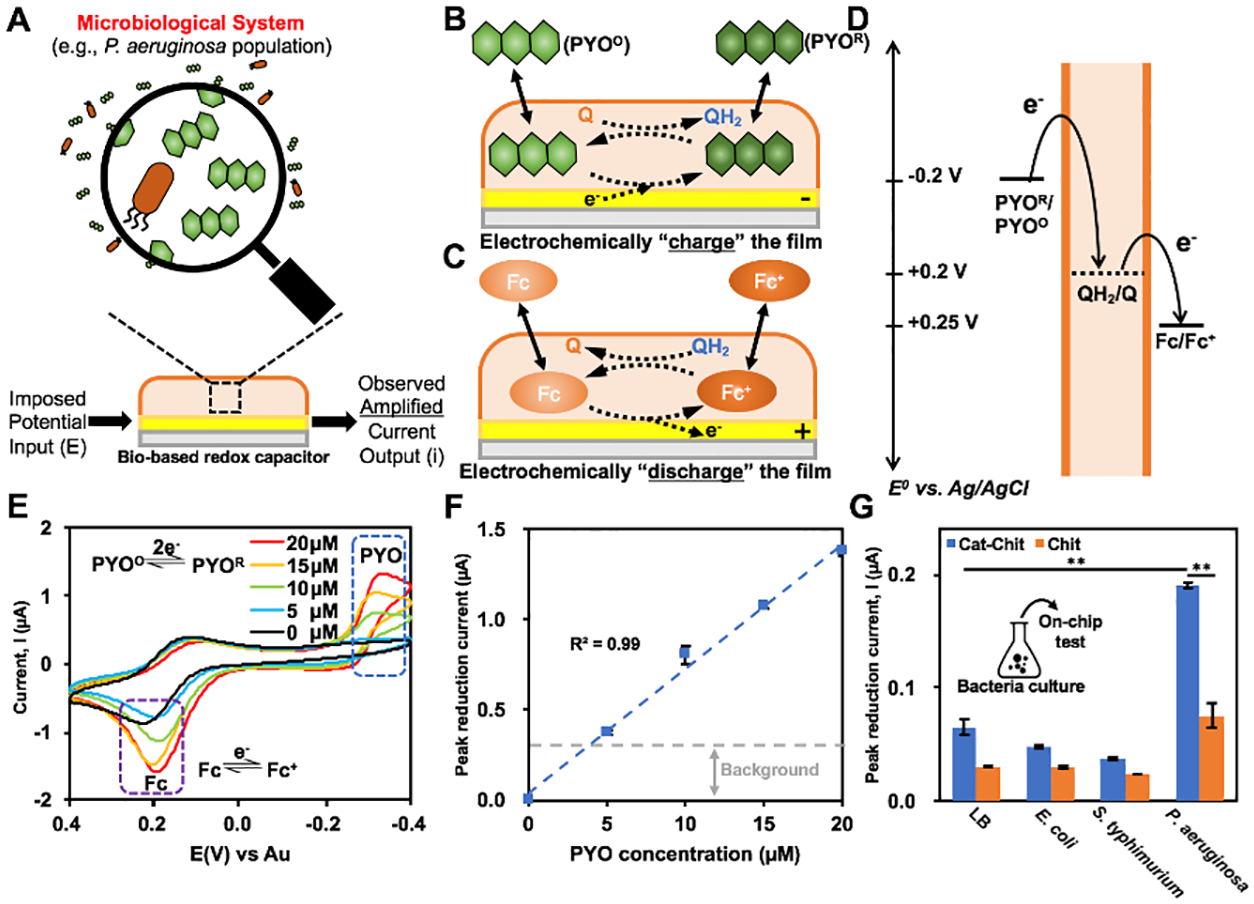
(A) Schematic illustrating the microbiological analysis using BBRC films made possible by amplifying electrochemical signals in the bacterial secretome. (B) Reductive redox-cycling between PYOO/PYOR and the BBRC film. (C) Oxidative redox-recycling between Fc+/Fc and the BBRC film. (D) Thermodynamics of electron transfer. (E) Cyclic voltammogram (CV) of PYOO in PB with concentrations from 0 μM to 20 μM. (F) Calibration curve of PYO measurement. (G) On-chip PYO measurements within LB and conditioned media (CM) from E. coli, S. Typhimurium and P. aeruginosa overnight cultures (**, p < 0.01). Results are compared between the molectronic sensor (Cat-Chit) and the control device (Chit). Q: quinone; QH2: catechol
