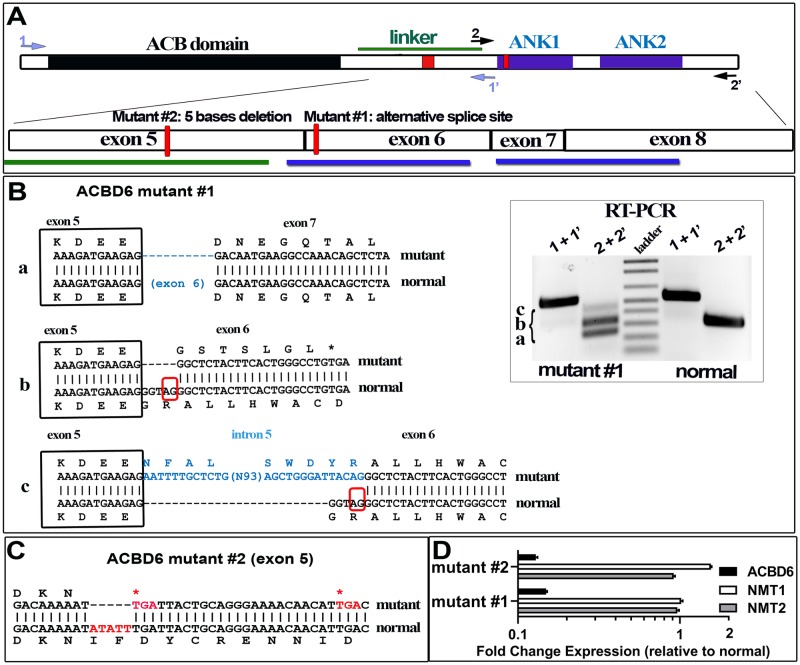
Fig 7. Spliced isoforms identification of human ACBD6-deficient fibroblasts.
Panel A. The usage of an alternative splice site in exon 6 (mutant #1) and the 5 bases deletion in exon 5 (mutant #2) are indicated as red boxes on the cartoon representation of ACBD6. The exon organization of the linker and the ANK-repeat motifs (ANK1 and ANK2) region is also shown. The positions of the two primer pairs (1/1’ and 2/2’) used for reversed transcription of ACBD6 mRNA are indicated. Panel B. Three cDNAs were identified with the RNA isolated from mutant #1 and are indicated as isoform a, b, and c. Separation of the cDNAs on 1.2% agarose gel is shown in the inset. Isoform a lacks exon 6 encoding the ANK1 motif; isoform b represents the splicing of exon 5 to the alternative splice acceptor site identified in exon 6, and result in the early translational stop removing the ANK1 and ANK2 motifs; isoform c is similar to isoform b but with an insertion of a sequence present in intron 5, and resulting in the disruption of ANK1. Because of the low level of expression of ACBD6 mRNA in those cells, the very low abundant isoform c might represent an immature pre-RNA of isoform b detected by end-point RT-PCR. Panel C. The five bases deletion affecting exon 5 of ACBD6 in mutant #2 is highlighted in red. The single isoform detected in these cells will produce a form truncated of the linker and ANK motifs. Panel D. Expression of ACBD6, NMT1 and NMT2 were determined by qRT-PCR, using ACTB as the reference mRNA. The values obtained with RNA isolated from the two mutant cells are reported relative to the values obtained with normal fibroblast. Note the logarithmic scale of the x axis. Error bars represent the standard deviations of values obtained from 4 measurements.