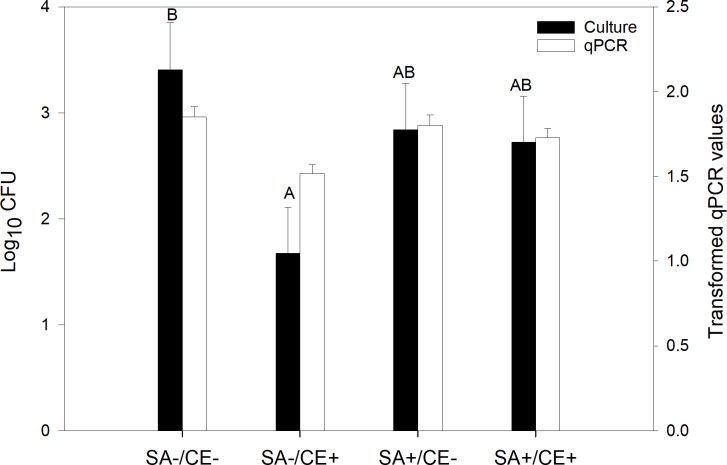
Fig 5. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli F4 shedding determined using culturing (black bars) and qPCR (white bars) in feces samples from piglets receiving a standard diet without chestnut extract (CE) nor sodium salicylate (SA) supplementation (SA-/CE-; N = 18), from piglets receiving a standard diet with CE and without SA supplementation (SA-/CE+; N = 18), from piglets receiving a standard diet supplemented with SA (SA+/CE-; N = 18), and from piglets receiving a standard diet supplemented with both CE and SA (SA+/CE+; N = 18).
From days 0‒4 post-infection, pigs from the SA+/CE-and SA+/CE+ groups were offered a daily dose of sodium salicylate (35 mg/kg BW per day, sodium salicylate, ReagentPlus®, S3007, Sigma-Aldrich Chemie GmbH; Buchs, Switzerland). From days 0‒4 post-infection, pigs from the SA-/CE-and SA-/CE+ groups were offered a daily dose of tap water. The CE- diet was a control standard starter diet, which was formulated according to the Swiss feeding recommendations for pigs (Agroscope, 2017). The CE+ diet was a CE-supplemented diet in which the wheat straw in the CE- diet was substituted for with 2% CE (Silvafeed Nutri P/ENC for Swine; Italy). Data are expressed as log10 (Colony Formant Units) for culturing and as transformed qPCR values according to: , where X represents the ng heat-labile toxin-DNA per g of feces dry matter for qPCR. P-values for SA × CE: P = 0.03 (culturing) and P = 0.19 for qPCR). A,B Bars carrying no common superscript differ at P < 0.05 for the culturing method.