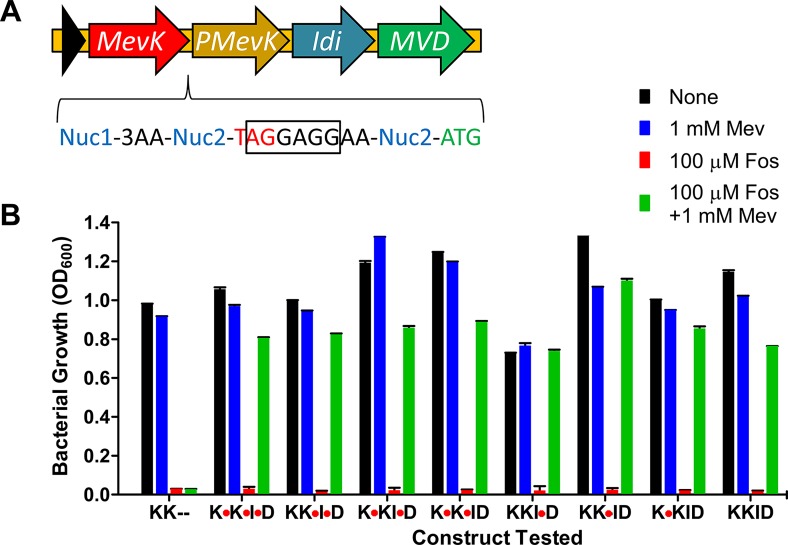
Fig 1. Design and validation of a multi-protein expression system for mevalonate pathway genes.
A) Streptococcus pneumoniae mevalonate kinase (mevK), Homo sapiens phosphomevalonate kinase (pmevK), E. coli isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase (idi), and S. pneumoniae mevalonate 5-diphosphate decarboxylase (mvd) were arranged for polycistronic expression in E. coli with a stop codon (red) and ribosomal binding site (black box) between each pair of genes. Digestion with a specific endonuclease (Nuc2) allowed these elements to be removed for expression of a multi-functional proteins linked by flexible three amino acid linkers (3AA). B) The eight possible ways of connecting the four genes (red octagons show retention of the stop codon) were tested by attempting to rescue the growth of E. coli inhibited with the isoprenoid synthesis inhibitor fosmidomycin (Fos). Successful growth in the presence of mevalonate (Mev) showed that all eight constructs rescued fosmidomycin inhibition in a mevalonate-dependent manner, while the negative control only containing the two kinases (KK—) did not.