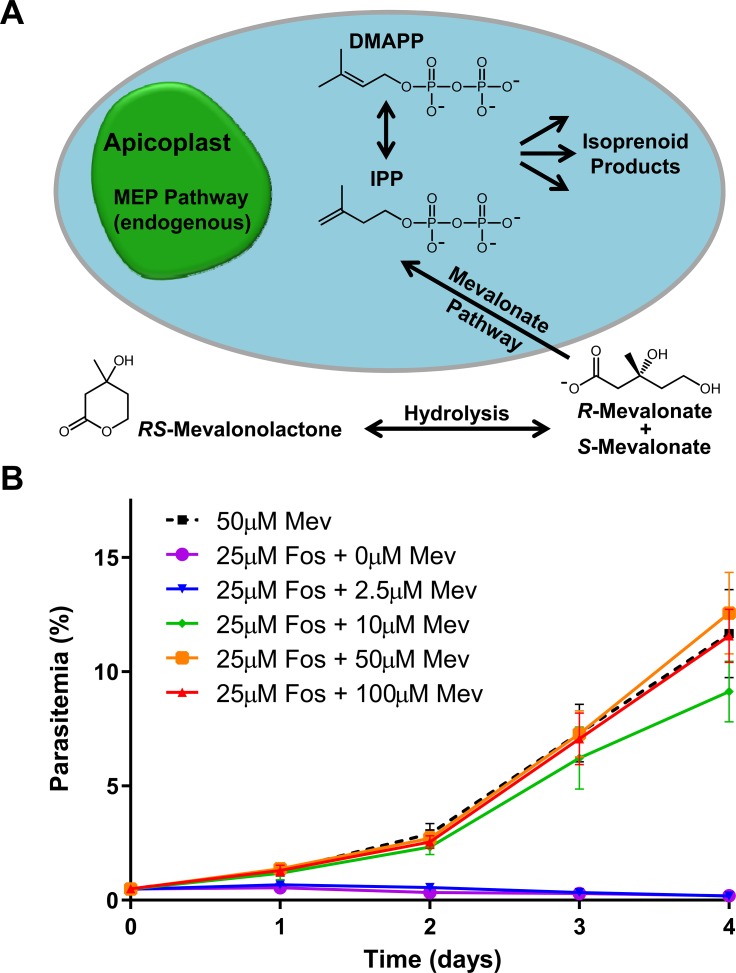
Fig 2. The MVA pathway bypasses fosmidomycin toxicity in PfMev parasites.
A) Diagram of the parasite cell showing that the endogenous MEP pathway is localized with the apicoplast organelle of the parasite, with IPP and DMAPP presumably being exported out of the organelle. We engineered the PfMev parasites to express four enzymes forming a MVA pathway in the cytosol capable of producing IPP and DMAPP from exogenous mevalonate supplied in the growth medium. B) PfMev parasites were treated with 25μM fosmidomycin (50x IC50), and supplemented with various concentrations of mevalonate, with growth compared to an untreated control. PfMev parasites grew to wild-type levels in the presence of a typically lethal concentration of fosmidomycin when supplemented with at least 10μM mevalonate, indicating usage of the engineered mevalonate pathway for the generation of essential isoprenoid precursors. PfMev parasites treated with fosmidomycin and not supplemented with mevalonate failed to grow. These data are from quadruplicate independent experiments, each conducted in quadruplicate with error bars representing the standard error of the mean (SEM).