Figure 2.
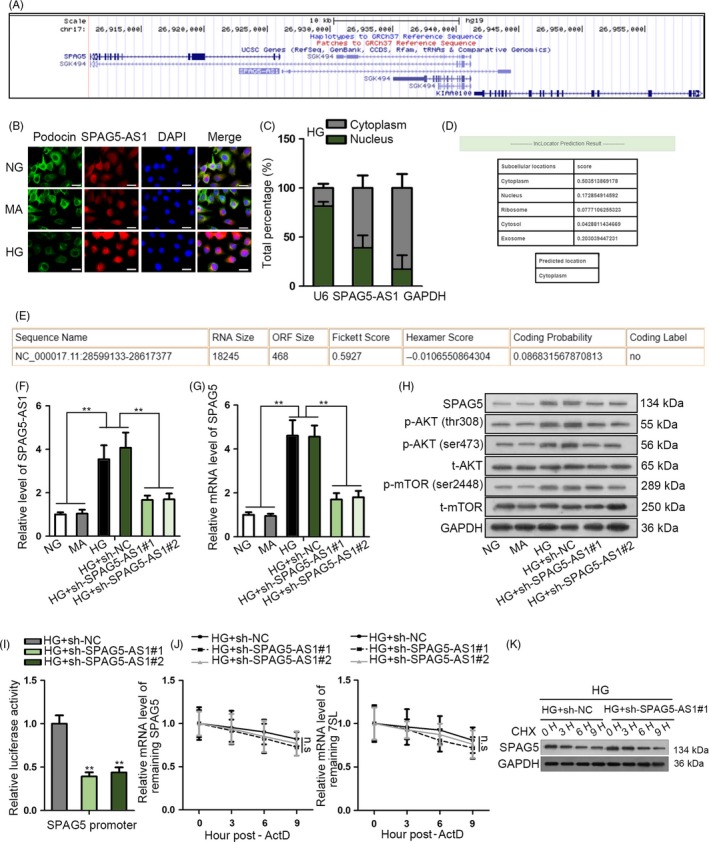
SPAG5‐AS1 positively regulated SPAG5 transcription and protein stability in HPCs. A, UCSC showed that genomic location of SPAG5‐AS1 was neighbour to SPAG5. B‐C, Abundance and localization of SPAG5‐AS1 were determined by FISH and nucleus‐cytoplasm separation assay in HPCs under HG treatment compared to the control groups. Expression of podocyte marker podocin in HPCs was detected by IF staining. Scale bar: 25 μm. D, Bioinformatics tool lncLocator predicted the SPAG5‐AS1 cytoplasmic localization. E, Result of online coding potential analysis tool CPAT for SPAG5‐AS1. F‐G, The mRNA levels of SPAG5‐AS1 and SPAG5 in HG‐treated HPCs after inhibiting SPAG5‐AS1. H, Western blot analysis for the regulation of SPAG5‐AS1 depletion on levels of SPAG5 and phosphorylated and total AKT and mTOR under HG treatment. I, Luciferase activity of SPAG5 promoter reporter in response to the decrease in SPAG5‐AS1 level was monitored under HG treatment. J‐K, The ActD and CHX treatments were used for detecting SPAG5 mRNA stability and the protein degradation of SPAG5 caused by sh‐SPAG5‐AS1 transfection in HG‐treated HPCs. All experiments were conducted in triplicates. Data are presented as mean ± SD. **P < .01
