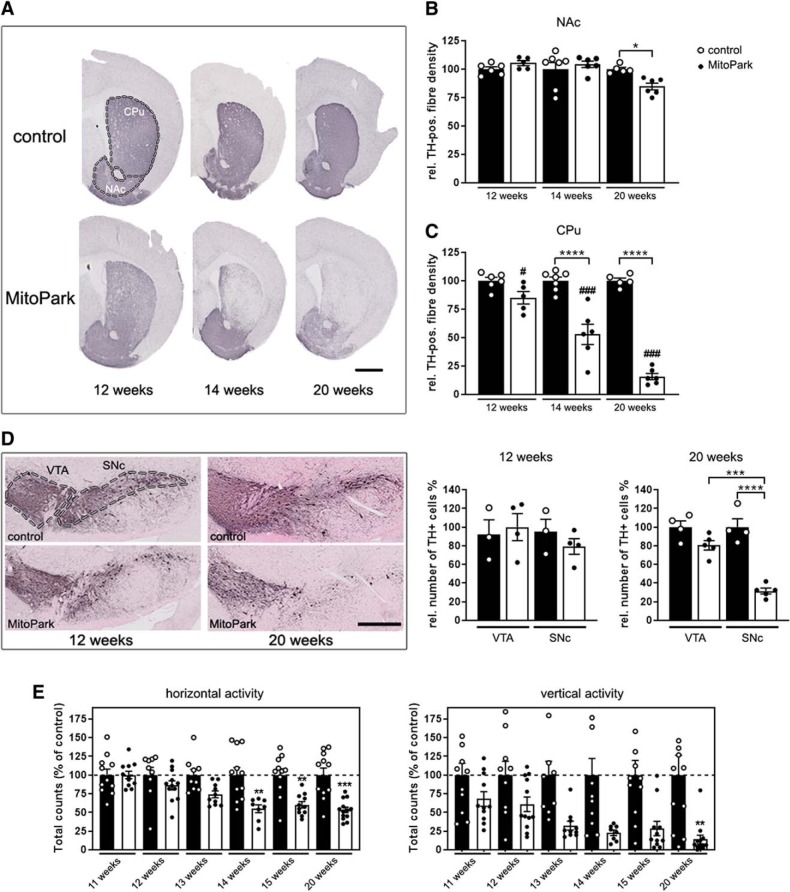
Figure 1.
Degeneration of the nigro-striatal system in MitoPark mice. A, Tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) immunohistochemistry in the striatum (CPu and NAc, marked by the dashed line) of 12-, 14-, and 20-week-old MitoPark and age-matched control mice. Scale bar, 1 mm. B, Quantification of the striatal TH signal revealed minor degeneration of dopaminergic projections with increasing age in the NAc of MitoPark mice (black dots on white bars). C, In contrast, there was a dramatic loss of the dopaminergic projections in the CPu of aging MitoPark mice (Control mice: n = 5–7, MitoPark mice: n = 5–6; # indicates significances between CPu and NAc of MitoPark mice). D, Immunohistochemical staining of TH-positive neurons in the VTA and SNc in 12- and 20-week-old MitoPark and control mice (VTA and SNc delimitated by dashed lines). Scale bar, 500 μm. DaN numbers (TH+ neurons) in both midbrain regions of MitoPark (black dots on white bars; n = 4–6) and control mice (white dots on black bars; n = 4) were estimated by stereological quantification. E, Beam break events are presented on the horizontal and vertical levels to show the spontaneous motoric activity of MitoPark mice (black dots on white bars; n = 8–13) compared with control mice (white dots on black bars; n = 9–11). Data are represented as mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, ###p < 0.001.