FIGURE 3.
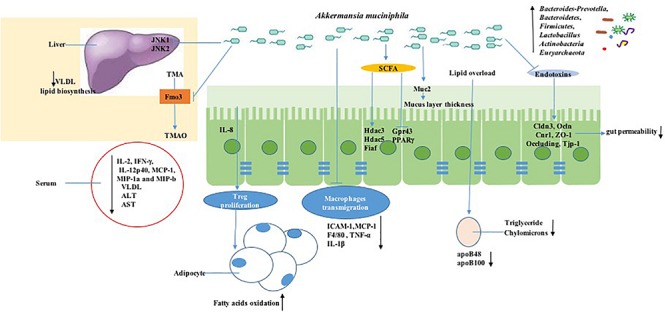
Mechanisms of signaling due to A. muciniphila action in obesity. A. muciniphila can decrease the serum level of inflammatory cytokines such as IL-2, IFN-γ, IL-12p40, and MCP-1. Meanwhile, A. muciniphila decreases the lipid overload process associated with the LDL receptor pathway by decreasing apoB48 and apoB100 on LDLs. Moreover, short-chain fatty acid production stimulated by A. muciniphila is involved in signaling to the host by inhibiting histone deacetylase (HDAC) or by activating G-protein-coupled receptors, which triggers other metabolic pathways, together resulting in immune stimulation including macrophage transmigration and Treg proliferation changes. A. muciniphila regulates the intestinal permeability and gut barrier by tight-junction proteins such as Claudin 3 (Cldn3), Occludi(Ocln), and Cannabinoid Receptor 1 (Cnr1) and reverses the high enzyme expression of flavin-containing monooxygenase 3 (FMO3), which modulates TMA conversion into TMAO in the liver.
