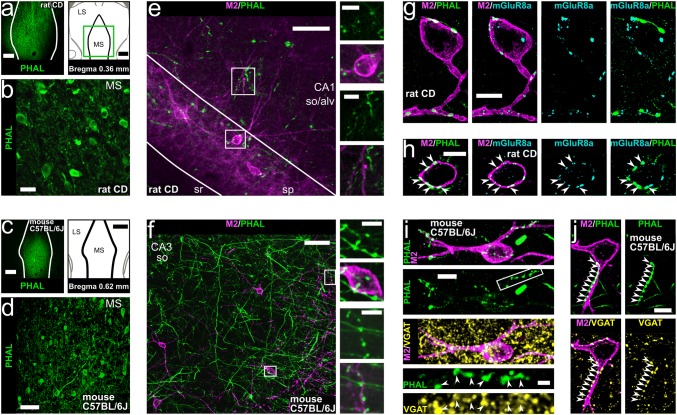
Fig. 3.
Hippocampal trilaminar cells are innervated by neurons of the medial septum. a–d Injection sites of the anterograde tracer PHAL (left in a–c, single optical sections, 20.8 μm) and tracer-labelled neurons in the medial septum of rat and mouse (b, d, maximum intensity projections, z stacks, heights 5.2 μm and 7.8 μm, respectively). e–f Axonal projections of PHAL-labelled medial septal neurons in areas CA1 and CA3 (maximum intensity projections, z stacks, heights 12.1 μm and 3.7 μm, respectively) in apposition to cell bodies and dendrites of M2+ neurons (insets). g–h The M2+ neurons postsynaptic to medial septal axon terminals are densely innervated by mGluR8a+ boutons identifying them as trilaminar cells (maximum intensity projections, z stacks, heights 3 μm and 0.8 μm). Note mGluR8a expression in some of the medial septal input terminals (arrowheads, h). i–j Trilaminar cells postsynaptic to medial septal axon terminals are densely innervated by GABAergic VGAT+ boutons (i maximum intensity projection, z stack, height 9.1 μm). Note VGAT expression in some of the medial septal input terminals next to trilaminar cells (j arrowheads, confocal microscopic single optical section, 0.5 μm). SD, Sprague–Dawley; MS, medial septum; LS, lateral septum; so, stratum oriens; alv, alveus; sp, stratum pyramidale; sr, stratum radiatum; +, immunopositive; scale bars 500 μm in a, 25 μm in b, 250 μm in c, 50 μm in d–f, 10 μm in g–j and insets of e, f