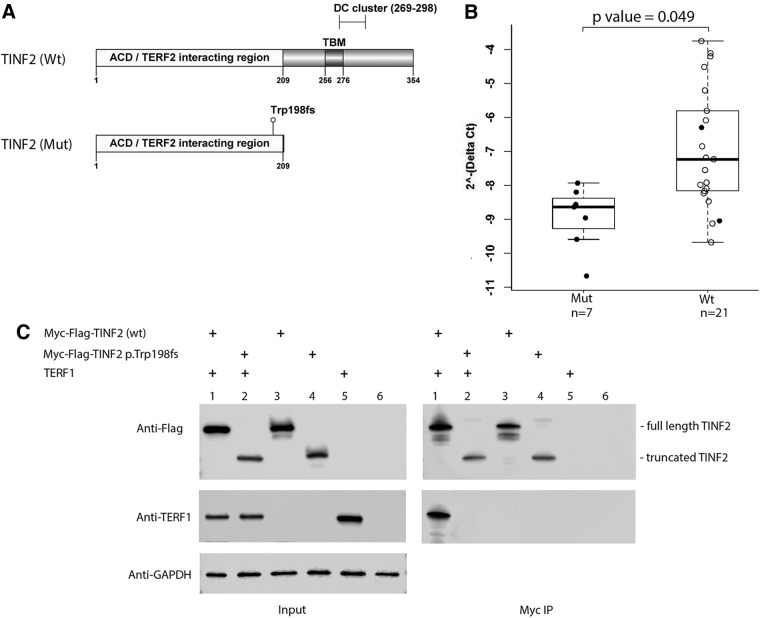
FIG. 2.
Analyses of the mutant TINF2. (A) Schematic of the mutant and the wild-type TINF2 protein structures. TBM, the TERF1 binding motif; DC cluster, the region with TINF2 mutations in the patients with short telomere syndromes. The numbers indicate the positions of the amino acids in TINF2. (B) Quantitative RT-PCRs were performed with RNAs from lymphoblastoid cell lines established from individuals as indicated. GAPDH was used as an internal control. Mut, individuals with the mutant TINF2; Wt, individuals with the wild-type TINF2. n, sample size; solid dots, individuals from one family. (C) Co-immunoprecipitation assay and Western blot. HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated plasmid DNAs (lanes 1–5). Co-immunoprecipitations (Myc IP) with protein extracts from transfected HEK293T cells and normal HEK293T cells (lane 6) were analyzed by Western blotting. The positions of the full length and the truncated TINF2 are marked. GAPDH serves as the loading control (Input). DC, dyskeratosis congenital; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; TBM, TERF1 binding motif.