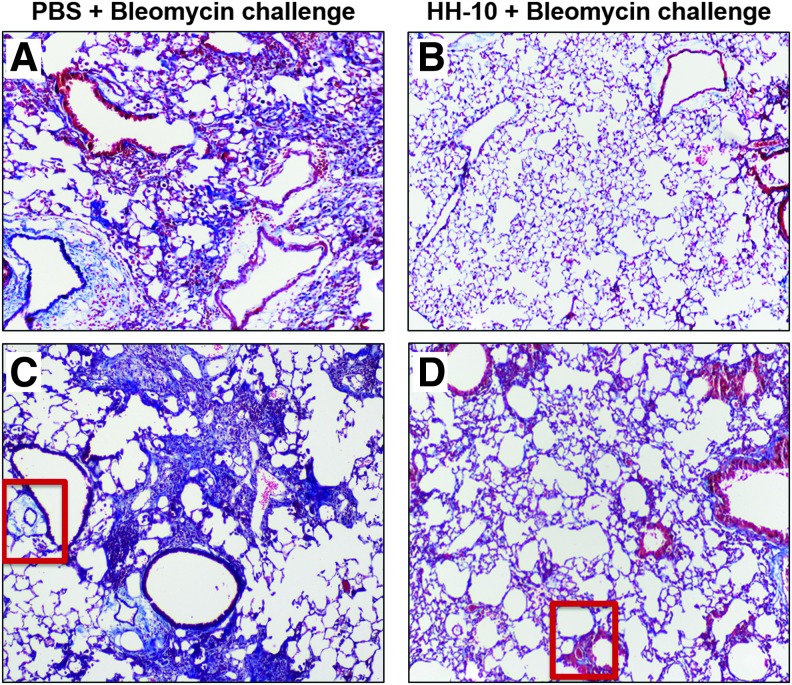
Figure 4.
(A–D) Representative histology of bleomycin-challenged murine lungs, with and without intranasal HH-10 hydrogel treatment. Intranasal administration of bleomycin induces pulmonary fibrosis in mice and is an established experimental model of human IPF. Compared to PBS/control-treated animals (A, C), 7 days of intranasal HH-10 (200 ng/mL IL-10 in a hyaluronan-based hydrogel) treatment (B, D) decreases the size and severity of fibrotic lesions in the lungs of bleomycin-challenged mice. Note also that the extent of perivascular fibrosis, as demonstrated by the extent of blue staining (red boxes) was also reduced by treatment with HH-10. Images show trichrome staining (top row: 4 × objective; bottom row: 40 × objective) of lung tissue sections of bleomycin-challenged treatment cohorts. IPF, Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sample images courtesy of S. Balaji and V. de Jesus Perez, with results as described in Shamskhou et al.59