FIG. 1.
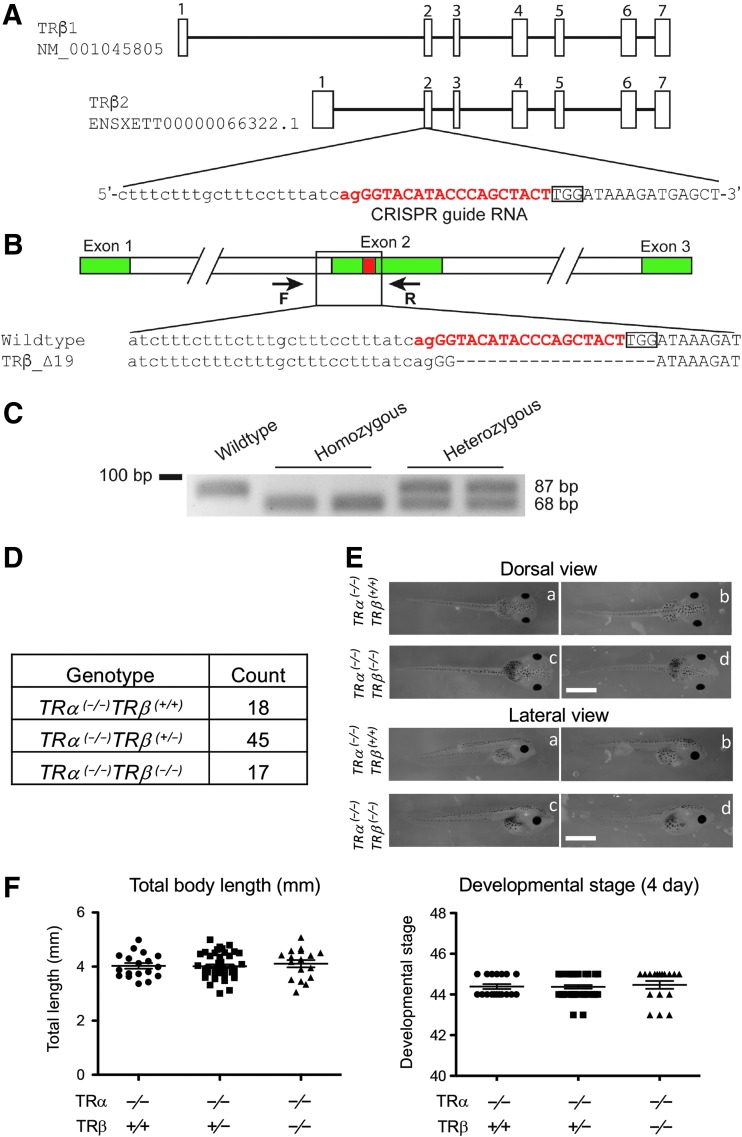
Knocking out both TR genes does not affect Xenopus tropicalis embryogenesis. (A) Genomic structure of the X. tropicalis TRβ gene and the CRISPR-sgRNA against X. tropicalis TRβ. There are two known transcripts for X. tropicalis TRβ, each with seven exons (boxes). The TRβ-specific sgRNA was designed to target exon 2, and the sgRNA sequences are shown in red. (B) Schematic diagram depicting the sequence of the sgRNA-targeted region in the WT and a TRβ-mutant (19 bases deletion) animals. Arrows represent primers used for genotyping: the forward primer F and the reverse primer R, respectively. (C) Representative examples of genotyping by PCR. Genotyping PCR was carried out on genomic DNA by using a common primer set, primer F and primer R. The presence of only upper (105 bp) or lower (86 bp) band in the gel indicates a WT or homozygous mutant animal, respectively, while the presence of both upper and lower band indicates a heterozygous mutant. (D) Mendelian distribution of four-day-old tadpoles from mating of two TRα (−/−)TRβ (+/−) animals. Genotyping PCR was carried out by using tail tip genomic DNA of four-day-old tadpoles, which were at stage 45/46, the onset of tadpole feeding, and the result was close to the expected Mendelian ratio. (E) Representative photos of four-day-old tadpoles of the WT or homozygous TRβ-knockout genotype in the homozygous TRα mutant background. The upper column is the dorsal view and the lower column is the lateral view. Lowercase letters in both columns indicate the same tadpole. Note that no obvious difference was present between the WT or homozygous TRβ tadpoles in the homozygous TRα mutant background. Scale bars: 1 mm. (F) Knocking out TRβ in the homozygous TRα mutant background does not affect the body length and developmental stage of four-day-old tadpoles. The data are shown as the mean, marked as a line, and SE. No significant difference was observed in both parameters for the three genotypes, indicating that removing TRβ has no effect on X. tropicalis embryogenesis. CRISPR, clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; SE, standard error; sgRNA, short guide RNA; T3, thyroid hormone; TR, T3 receptor; WT, wild type.