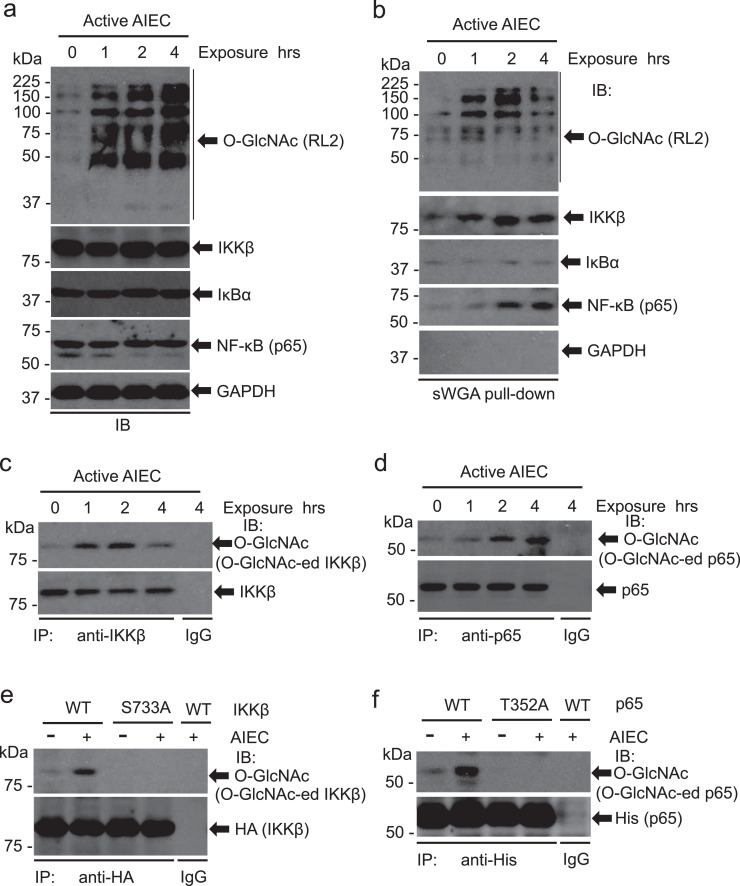
Fig. 4.
IKKβ and NF-kappa B are O-Glycosylated in active AIEC LF82-infected cells. HCT116 cells were infected with AIEC LF82 (MOI = 10) for the indicated time. (a) Whole cell extracts were analyzed with immunoblots for O-GlcNAc, IKKβ, IκBα, and NF-κB (p65) with respective antibodies. GAPDH serves as a loading control. (b) O-GlcNAcylated proteins in HCT116 cells infected with AIEC LF82 were pulled down with sWGA beads. IKKβ, IκBα, NF-κB (p65), and O-GlcNAc in the pull-down complexes were detected with immunoblotting. (c, d) IKKβ and NF-κB (p65) are O-GlcNAcylated. IKKβ (c) and NF-κB (p65) (d) in HCT116 cells infected with AIEC LF82 were immunoprecipiated with anti-IKKβ or anti-NF-κB (p65) antibody. The O-GlcNAcylated IKKβ and NF-κB (p65) were detected with an O-GlcNAc monoclonal antibody, RL2. (e) HCT116 cells were transduced with pcDNA3/HA-IKKβ or pcDNA3/HA-IKKβ S733A for 48 h. The cells were then exposed to AIEC LF82 (MOI = 10) for 4 h before whole cell extracts were collected for the co-IP assay as describled in (c). (f) HCT116 cells were transduced with pcDNA3/His-p65 or pcDNA3/His-p65 T352A for 48 h. The cells were then exposed to AIEC LF82 (MOI = 10) for 4 h before whole cell extracts were harvested for the co-IP assay as describled in (d).