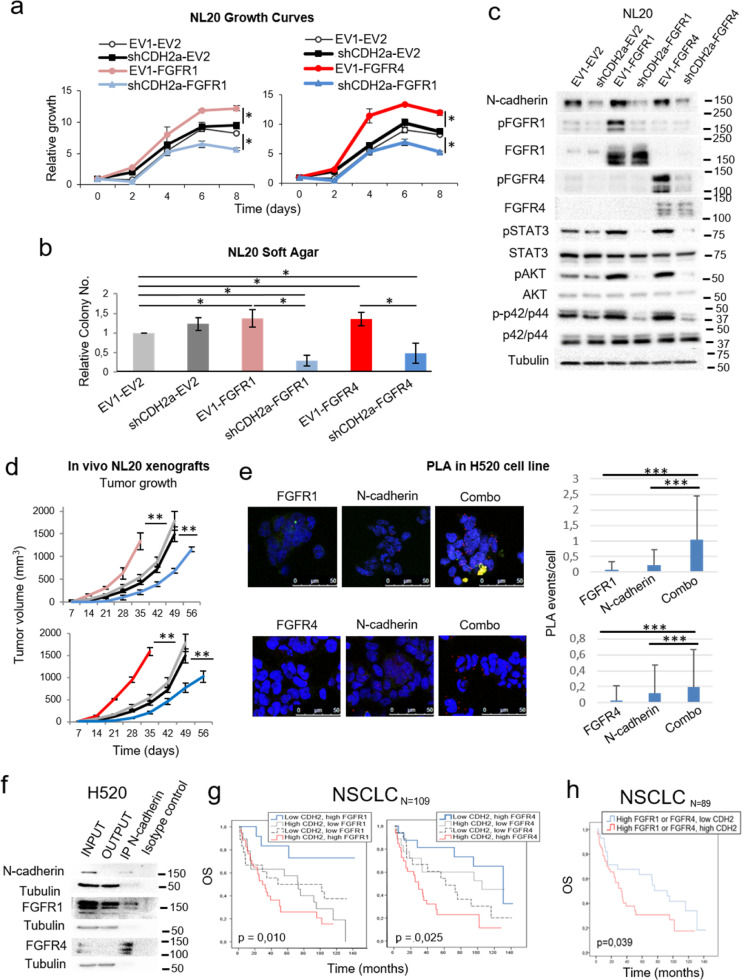
Fig. 4.
Effects of N-cadherin on the pro-oncogenic role of FGFR1 and FGFR4 and the interaction of N-cadherin with FGFR1 and FGFR4. See also Supplementary Figure S4. (a) 0.5% FBS growth curves for FGFR1-overexpressing and N-cadherin-silenced (left) or FGFR4-overexpressing and N-cadherin-silenced (right) NL20 cells. (b) Soft agar assays of FGFR-overexpressing and N-cadherin-silenced NL20 cells. (c) Western blot analysis of the activation of FGFR-related signalling pathways in these cell lines. (d) Xenograft tumour volumes of the FGFR1, FGFR4 and N-cadherin interaction models in the immortalised NL20 cell line. (e) Proximity ligation assays (PLA) to assess the physical interaction of N-cadherin with FGFR1 (upper panel) or FGFR4 (lower panel). The interactions detected were quantified and normalised by cell number for each condition. As controls to distinguish signal from noise, interactions were quantified in the single antibody conditions (labelled as “N-cadherin”, “FGFR1” and “FGFR4”). To assess the interaction between the two proteins, both antibodies were used, either N-cadherin + FGFR1 (upper panel) or N-cadherin + FGFR4 (lower panel), in the condition labelled as “combo”. Representative images and quantifications are shown. (f) Co-immunoprecipitation of N-cadherin with FGFR1 and with FGFR4 in the H520 cell line. (g) Kaplan-Meier curves of overall survival (OS) for the entire NSCLC patient cohort (N = 109). Patients were grouped based on FGFR1 and N-cadherin expression levels or on FGFR4 and N-cadherin expression levels. (h) OS curve of patients in the cohort with high expression of FGFR1 and/or FGFR4 stratified by N-cadherin expression levels. In each analysis, for the FGFR1 and N-cadherin genes, the cut-off point was the median mRNA expression value for that variable. For FGFR4, the cut-off point was the first-quartile mRNA expression value in the TCGA adenocarcinoma cohort. The Kaplan-Meier method was used for survival analyses of the clinical data and cell line xenograft experiments, with a Cox proportional hazards model used to adjust for explanatory variables. A log Rank analysis was used to analyse differences in survival between groups. To obtain the hazard ratio values, the Cox proportional hazards model was used. All in vitro experiments were reproduced a minimum of three times in the laboratory, and three technical replicates were obtained for each experiment. For growth curves and western blots, a representative figure/image is shown. On the growth curves, the means and standard deviations of the technical replicates are shown. In the soft agar assays, all values were normalised to the empty vector control, and the mean and standard deviation of all the normalised replicates are presented. N-cadherin silencing was performed using two different shRNAs. Results generated with the alternative shRNA are shown in Supplementary Figure S3 c-e. p-values were obtained with the two-sided Mann-Whitney U test and are indicated by asterisks (* p<0.05; ** p<0.01; *** p<0.001). EV1 = empty vector 1, EV2 = empty vector 2, FGFR1 = FGFR1-overexpressing, FGFR4 = FGFR4-overexpressing, CDH2 = N-cadherin-overexpressing, scramble = scrambled shRNA control, shCDH2 = silenced with N-cadherin shRNA. Western blot molecular weight references are indicated to the right of the images.