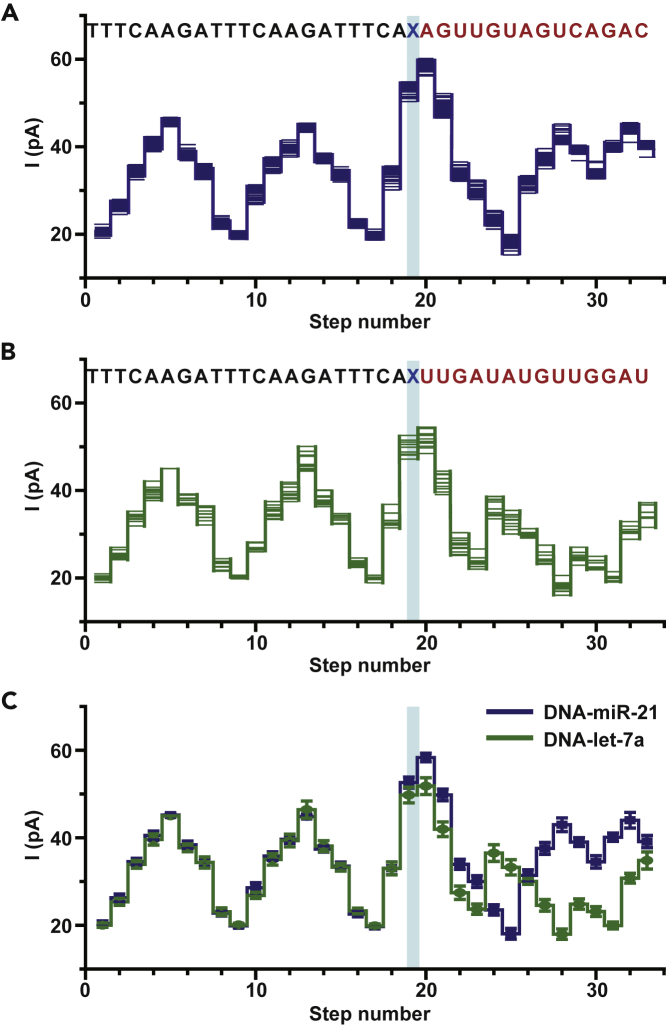
Figure 2.
Identification of miRNAs Using NIPSS
Chimeric template strands containing miRNA-21 and Let-7a sequences were custom synthesized (Table S1) and directly sequenced by NIPSS.
(A) Overlay of multiple time-normalized events (N = 24) from the DNA-miR-21 results acquired by NIPSS.
(B) Overlay of multiple time-normalized events (N = 12) from the DNA-let-7a results acquired by NIPSS. (A, B) The corresponding sequences (DNA-miR-21 or DNA-Let-7a, 3′-5′ convention) are aligned above the plots. The DNA segments are marked in black and the miRNA segments are marked in red. The abasic site (X, blue), which separates the DNA and miRNA segments, acts as a signal marker to identify the sequence transition from reading DNA to miRNA during NIPSS.
(C) Consensus sequencing results in comparison between DNA-miR-21 and DNA-let-7a. The mean and standard deviation values are derived from time-normalized events, as demonstrated in A and B. The DNA part of the NIPSS results shows great alignment in all steps between both templates. However, the miRNA segment of the signals shows significant variations, starting from the step marked with the blue stripe. Blue stripes in (A–C) mark the sequencing step of TCAX, which is the first quadromer sequence containing the abasic residue when acquired by NIPSS.
See also Table S1, Figures S5 and S6.