Figure 4.
Direct N6-methyladenosine (m6A) Mapping Using NIPSS
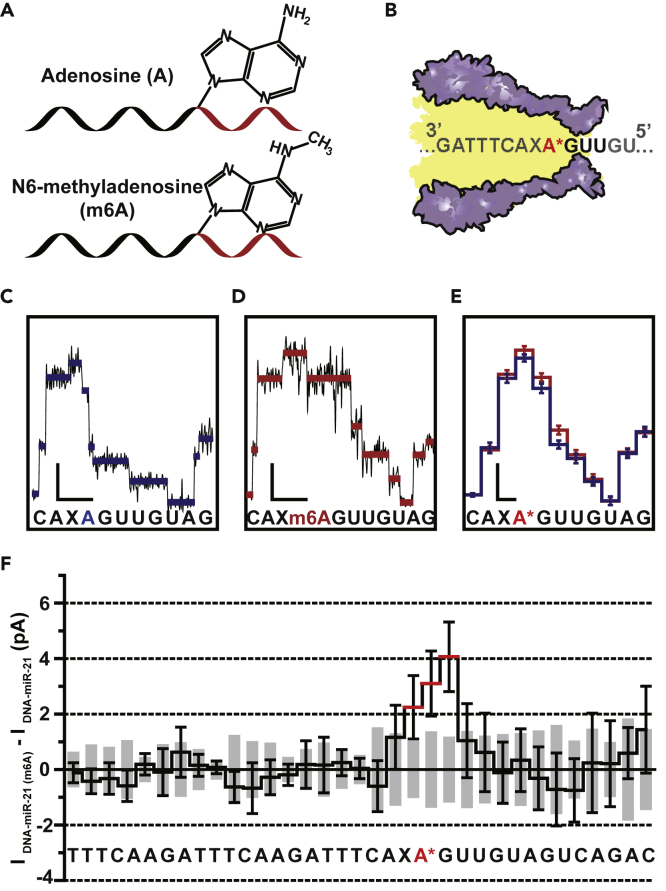
(A) Schematic diagram of chimeric template strands containing canonical adenosine (A) or N6-methyladenosine (m6A). A single “A” or “m6A” is embedded in different chimeric strands (top: DNA-miR-21, bottom: DNA-miR-21(m6A), Table S1) for NIPSS sequencing, where its chemical structure and location is annotated. Black and red segments represent the DNA and the miRNA part of the strand.
(B) Schematic diagram of NIPSS sequencing of miRNA containing “A” or “m6A” nucleotides. A∗ within the sequence context represents the “A” or “m6A” nucleotide within the strand.
(C) A representative current trace of DNA-miR-21 sequenced by NIPSS. Blue lines represent extracted mean current values from each step. The corresponding sequence context is aligned below in which a canonical adenosine is marked in blue.
(D) A representative current trace when DNA-miR-21(m6A) is sequenced by NIPSS. Red lines represent extracted mean current values from each step. The corresponding sequence context is aligned below, from which a N6-methyladenosine is marked in red. Scale bars in C and D represents 10 pA (current, vertical) and 50 ms (time, horizontal), respectively.
(E) Consensus sequencing results in comparison between DNA-miR-21 and DNA-miR-21(m6A). The means and standard deviations were derived from 24 independent events. A∗ within the sequence context below the results represents either A or m6A.
(F) Current differences between NIPSS results of DNA-miR-21 and DNA-miR-21(m6A). These differences were derived by calculating from the mean values of 24 events from each strand, with the associated sequence aligned below. The standard deviation values of DNA-miR-21 are demonstrated with gray column, and the standard deviation of DNA-miR-21(m6A) is demonstrated with black error bars. The m6A modification results in a signal variation when m6A containing sequence quadromers were read by the nanopore constriction. Due to the limited spatial resolution of MspA, a single m6A modification results in detectable signal fluctuations within three current steps as marked by red lines.
See also Table S1, Figures S9 and S10.