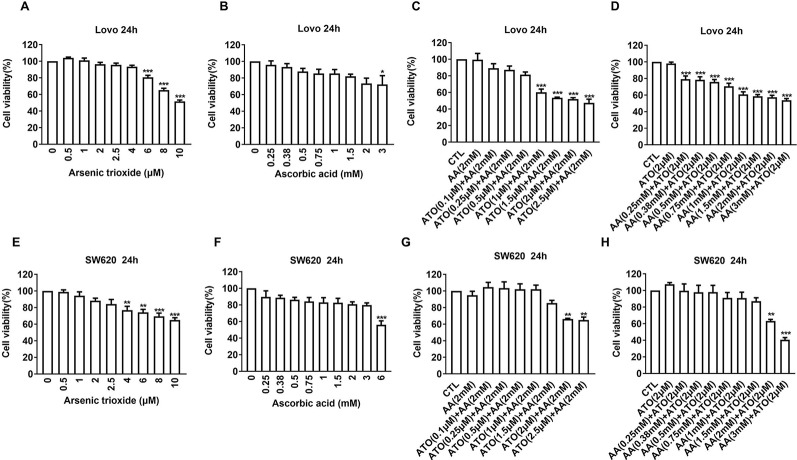
Figure 1.
Effects of ascorbic acid (AA), arsenic trioxide (ATO) alone, or co-administration on viability of colorectal cancer (CRC) cell lines. (A) Inhibitory effects of ATO alone on viability of LOVO cells. (B) Inhibitory effects of AA alone on viability of LOVO cells. (C) Facilitating effects of ATO on the suppression of LOVO cell viability induced by AA (2 mM). (D) Facilitating effects of AA on the suppression of LOVO cell viability induced by ATO (2 μM). (E) Inhibitory effects of ATO alone on viability of SW620 cells. (F) Inhibitory effects of AA alone on viability of SW620 cells. (G) Facilitating effects of ATO on the suppression of SW620 cell viability induced by AA (2 mM). (H) Facilitating effects of AA on the suppression of SW620 cell viability induced by ATO (2 μM). Relative or percent cell viability was determined by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA.