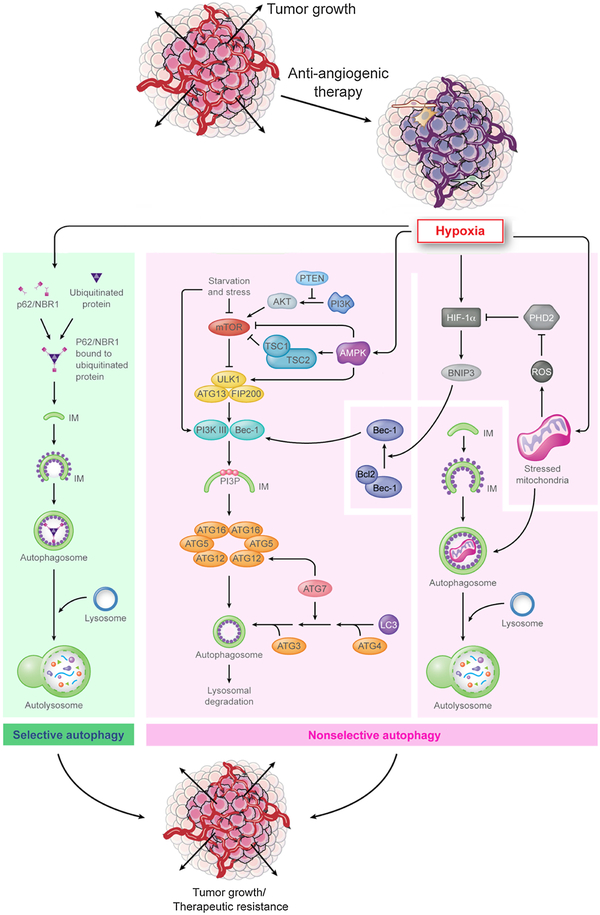
Fig. 2. Mechanisms underlying autophagy-mediated resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy.
Hypoxia results in anti-angiogenic therapy resistance by either selective autophagy (green), that is mediated by p62/NBR1, which sequesters targeted protein aggregates for autophagy, or by (B) non-selective autophagy (pink), which is mediated by two mechanisms (i) First is driven by HIF-1α that activates downstream mediators such as BNIP3. This mediator interacts with Beclin-1 and activates downstream autophagy pathways. Alternatively, hypoxia-induced mitochondrial stress can lead to autophagy activation. (ii) Second, starvation and cellular stress can modulate the Akt/mTOR pathway that can subsequently activate the autophagy pathway as an adaptive mechanism. Additionally, hypoxia can directly activate AMPK that interacts with the Akt/mTOR pathway and leads to activation of autophagy.